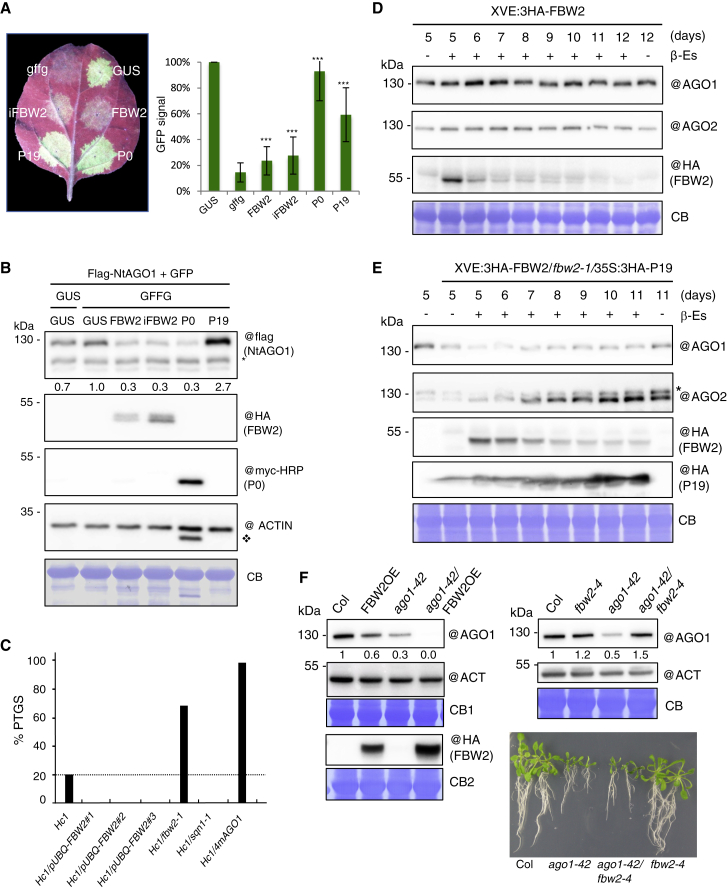
Figure 3.
Function of FBW2 in RNA silencing
(A) FBW2 is a weak endogenous suppressor of RNA silencing (based on two biological replicates). Left: picture of a N. benthamiana leaf 72 h after infiltration with agrobacteria harboring a 35S:Flag-NtAGO1 and a 35S:GFP construct plus either the following constructs: 35S:GUS or 35S:GFFG (GFP mRNA hairpin) together with either 35S:3HA-FBW2 (only the coding sequence), 35S:3HA-iFBW2 (coding sequence including an intron), 35S:P0-6myc, or 35S:P19. Right: the intensity of GFP signal in the infiltration area was measured with an Ettan DIGE imager (GE healthcare) and normalized to the GFP control condition. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (t test) compared with GFFG.
(B) Western blot of protein extracts from tissues sampled 72 h after agro-infiltration (shown in [A]). CB staining and ACTIN protein level were used as a loading control. @ indicates hybridization with the corresponding antibodies. NtAGO1 signal was quantified by ImageJ, normalized to the corresponding CB. Numbers are indicated below the panel as relative to the control set at 1.0. ∗Non-specific band; ❖remaining signal from P0-6myc hybridization.
(C) Modulating FBW2 level impacts transgene S-PTGS efficiency. GUS activity was measured in leaves of 8-week-old plants of the indicated genotypes. For each genotype, 96 plants (from three biological replicates of 32 plants each) were analyzed. S-PTGS efficiency is expressed as the percentage of plants exhibiting GUS activity below 50 FLUO/min/μg.
(D and E) Kinetic analysis of transgenic Arabidopsis Col-0 XVE:3HA-FBW2 (D) (based on three biological replicates) and XVE:3HA-FBW2/fbw2-1/35S:3HA-P19 (E) lines (based on one biological replicate). Western blots of protein extracts from 5- to 11- or 12-day-old seedlings grown on MS medium supplemented with DMSO (−) or β-Es (10 μM,+). Note that since P19 is a powerful silencing suppressor; it allowed maintaining the expression of 3HA-FBW2 for a longer time. CB staining was used as loading control, and the “@” symbol indicates hybridization with the corresponding antibodies.
(F) FBW2-mediated degradation of the AGO1-42 mutant protein impaired in sRNA loading (based on two biological replicates). Immunoblot analysis of AGO1 protein contents in the ago1-42 mutant background when FBW2 is overexpressed (left) or mutated (right). Seedlings grown on MS medium were harvested at 15 days, and protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using AGO1- and ACTIN-specific antibodies and the HA antibody for detecting FBW2. CB staining was used as loading controls (CB1 corresponds to AGO1 and ACTIN and CB2 to 3HA-FBW2 at the left). AGO1 signal was quantified by ImageJ and normalized to the corresponding ACTIN signal. Numbers below panels are indicated as relative to Col-0 set at 1.0. Bottom right: pictures of 25-day-old in vitro-grown seedlings of the indicated genotypes.