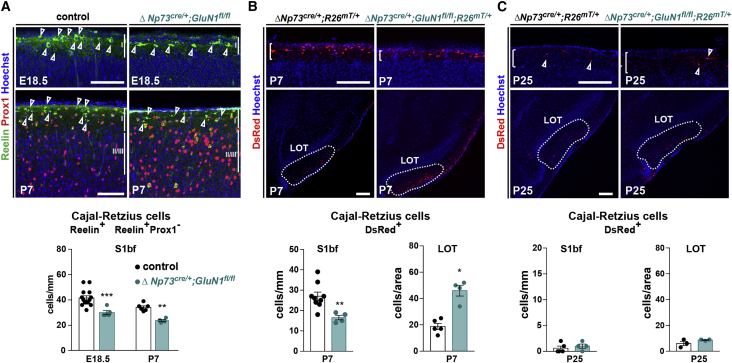
Figure 2.
CRc density is maintained through a GluN1-dependent distribution and a GluN1-independent elimination
(A) Confocal images of coronal sections in the barrel cortex (S1bf) of E18.5 and P7 controls and ΔNp73cre/+;GluN1fl/fl mutants. CRc are identified at embryonic stages as Reelin+ cells and postnatally as Reelin+Prox1− cells (top). Quantification of CRc density (cells/mm of L1 length) (E18.5: n = 14 for controls, n = 5 for mutants; P7: n = 6 for controls, n = 4 for mutants) (bottom).
(B) Confocal images of coronal sections in the barrel cortex (S1bf) and lateral olfactory tract (LOT) of P7 ΔNp73cre/+;R26mT/+ controls and ΔNp73cre/+;GluN1fl/fl;R26mT/+ mutants. White brackets delineate L1, and the dotted line highlights the LOT (top). Quantification of CRc density L1 S1bf (cells/mm) and in the LOT (cells/area LOT, see Methods details) (bottom) (L1: n = 9 controls, n = 4 mutants; LOT: n = 5 controls, n = 4 mutants).
(C) Confocal images of coronal sections in the barrel cortex (S1bf) (top) and LOT (bottom) of P25 controls and ΔNp73cre/+;GluN1fl/fl;R26mT/+ mutants. White brackets delineate L1, and the dotted line highlights the LOT (top). Quantification of CRc density in L1 (cells/mm) and in the LOT (cells/area lot) (bottom) (L1: n = 5 controls, n = 4 mutants; LOT: n = 3 controls, n = 3 mutants).
Values are expressed as means ± SEMs, 2-way ANOVA test with Sidak’s multiple comparison correction in (A) and Mann-Whitney U tests in (B and C). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Scale bars represent 100 μm in (A) and 200 μm in (B and C).