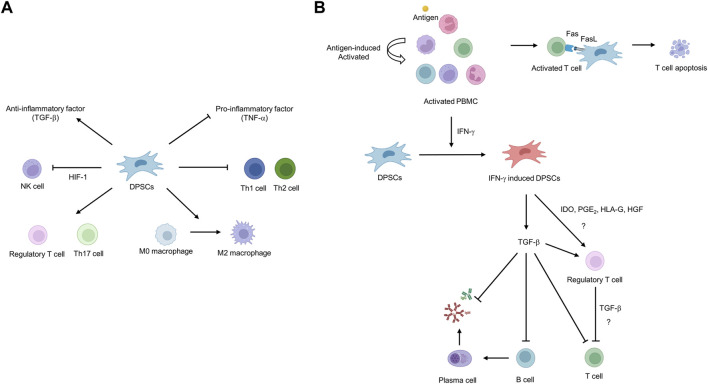
FIGURE 3.
Schematic diagram of the immunosuppressive potential of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). (A) DPSCs can inhibit the proliferation of natural killer (NK), T helper 1 (Th1), and T helper 2 (Th2) cells and the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α. In addition, DPSCs induce the proliferation of regulatory T cells (Tregs)/T helper 17 (Th17) cells and differentiation toward macrophage M2 phenotype and secrete anti-inflammatory factors such as TGF-β. (B) Fas ligand expressed in DPSCs induces T-cell apoptosis through Fas apoptotic pathway. IFN-γ secreted from hyper-activated T cells primes DPSCs to secrete TGF-β, resulting in immunosuppressive ability.