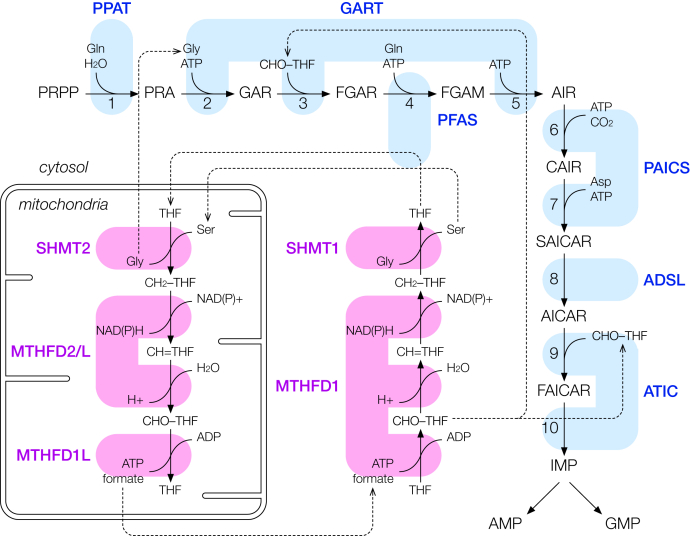
Figure 1.
Schematic of the human de novo purine biosynthesis (DNPB) pathway. The six DNPB enzymes (cyan) convert phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to inosine monophosphate (IMP) in a sequence of 10 reactions: amidophosphoribosyltransferase (PPAT) converts PRPP to 5-phosphoribosylamine (PRA); PRA is converted by trifunctional phosphoribosylglycinamide synthetase/formyltransferase/phosphoribosylaminoimidazole synthetase (GART) to glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR), and then to phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycineamide (FGAR); phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase (PFAS) converts FGAR to 5-phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine (FGAM), which is then converted by GART to 5-aminoimidazole ribotide (AIR); AIR is converted by bifunctional phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase/succinocarboxamide synthetase (PAICS) to 5-phosphoribosyl-4-carboxy-5-aminoimidazole (CAIR), and then to phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide (SAICAR); SAICAR is converted to 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) by adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL); finally, AICAR is converted to 5-formamidoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribotide (FAICAR) and then IMP by the bifunctional 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase/IMP cyclohydrolase (ATIC). Also shown (magenta) are the mitochondrial (serine hydroxymethyltransferase [SHMT2], bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase [MTHFD2/2L], formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase [MTHFD1L]) and cytosolic (serine hydroxymethyltransferase ([SHMT1], trifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase/formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase [MTHFD1]) one-carbon metabolism enzymes responsible for the interconversion between tetrahydrofolate (THF), 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (CH2-THF), 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate (CH=THF), and 10-formyltetrahydrofolate (CHO-THF)—the last being a necessary cofactor for DNPB.