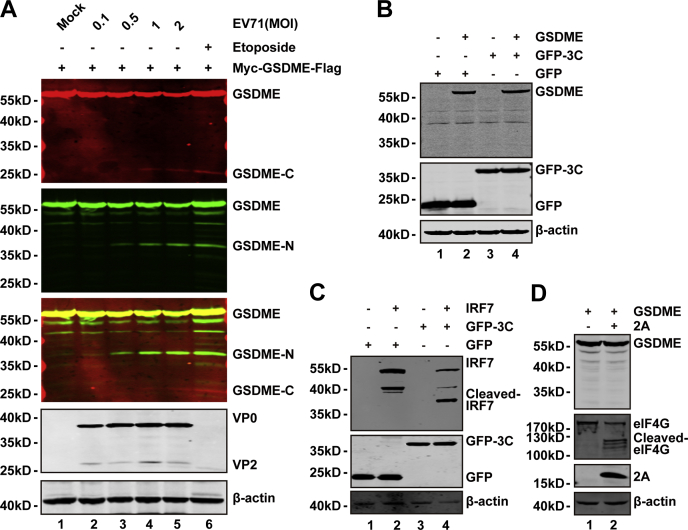
Figure 3.
EV71-mediated cleavage of GSDME is independent on 2A and 3C proteases.A, 293T cells were transfected with a plasmid that encoded Myc-GSDME-FLAG (lanes 1–6). At 24 h after transfection, the cells were mocked infected or infected with increasing doses of EV71. At 24 h after infection, cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies using the LI-COR Odyssey Dual-Color System (LI-COR). Antibodies that recognized Myc-GSDME-FLAG (Myc, N-terminal region of GSDME, 800 nm, green; FLAG, C-terminal region of GSDME, 680 nm, red) were used. The merged images of the two channels are shown below (yellow). EV71 was detected by using an antibody that recognized VP0 and VP2. β-actin was detected as a loading control. Etoposide was used as a control. B, 293T cells were transfected with plasmids that encoded GSDME (lanes 2 and 4) and GFP (lanes 1 and 2) or GFP-3C (lanes 3 and 4). At 24 h after transfection, the cells were prepared for Western blotting analyses using antibodies against Myc, GFP, and β-actin. C, 293T cells were transfected with plasmids that encoded IRF7 (lanes 2 and 4) along with GFP (lanes 1 and 2) or GFP-3C (lanes 3 and 4). Cells were analyzed as described in (B). D, 293T cells were transfected with a plasmid that encoded GSDME along with a control plasmid or pcDNA3.1-IRES-2A plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against Myc, V5, and eIF4G. Data are representative of three independent experiments. eIF4G, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G; EV71, enterovirus 71; GSDME, gasdermin E; IRF7, interferon regulatory factor 7.