FIGURE 1. EAE mice have increased susceptibility to sepsis-induced mortality.
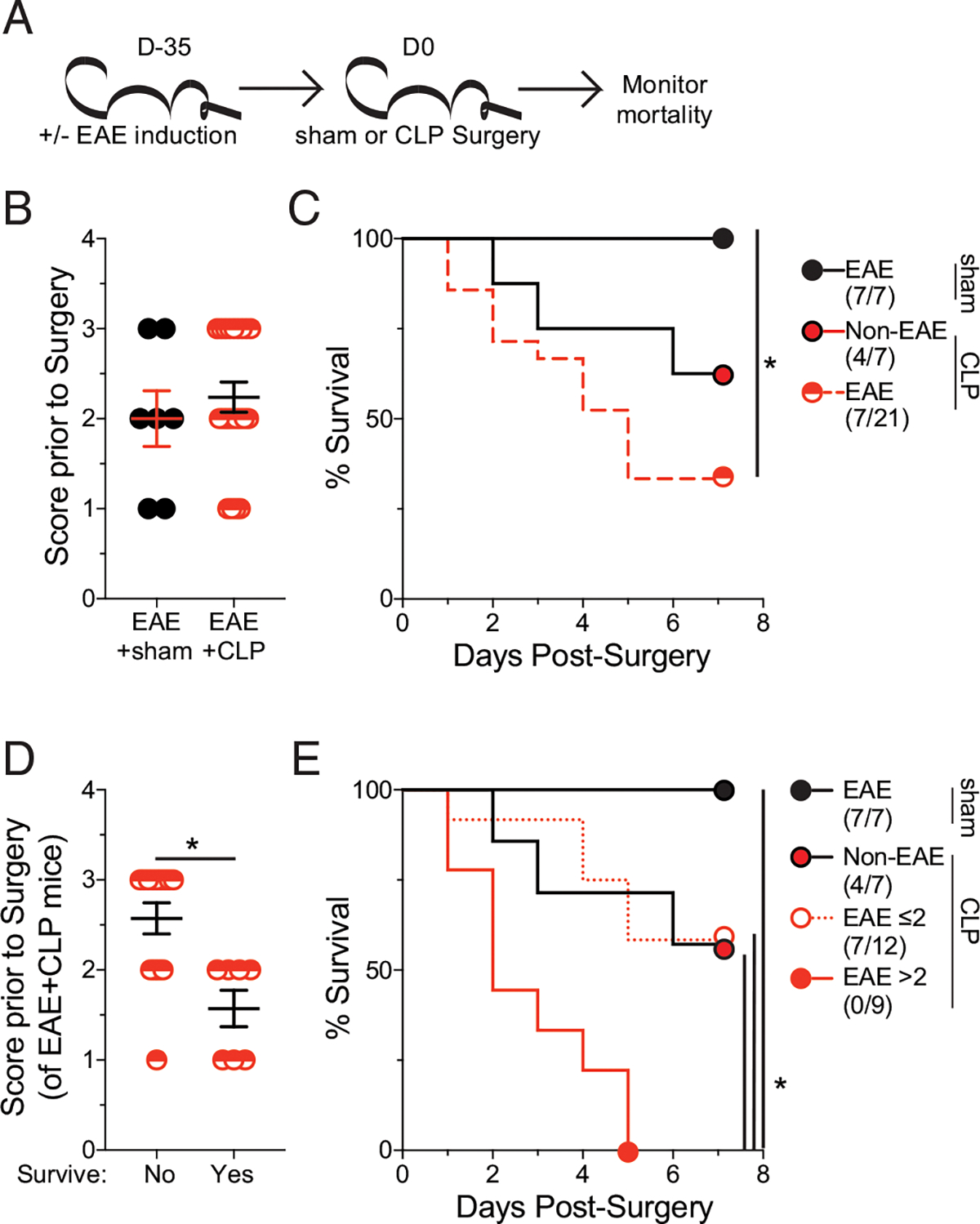
(A) Experimental design: C57BL/6 mice were immunized with MOG35–35 to induce EAE. EAE mice underwent either sham or CLP 35 d after EAE induction followed by assessment of mortality age-matched nonimmunized (non-EAE) underwent CLP surgery at the same time. (B) EAE clinical scores of mice prior to either sham or CLP surgery. (C) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of EAE mice that underwent sham (black closed circle) or CLP (red semicircle) surgery and non-EAE mice that underwent CLP surgery (red closed circle with black outline). (D) EAE clinical scores prior to surgery of EAE mice that either succumbed to or survived the septic insult. (E) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of EAE mice that underwent sham (black circle), had an EAE score ≤2 prior to CLP (white circle with red outline), or had an EAE score >2 prior to CLP (red closed circle with red outline) surgery and non-EAE mice that underwent CLP surgery (red closed circle with black outline). Data are cumulative of two independent experiments with 7–21 mice per group. Error bars represent SEM. *p < 0.05.
