Figure 4:
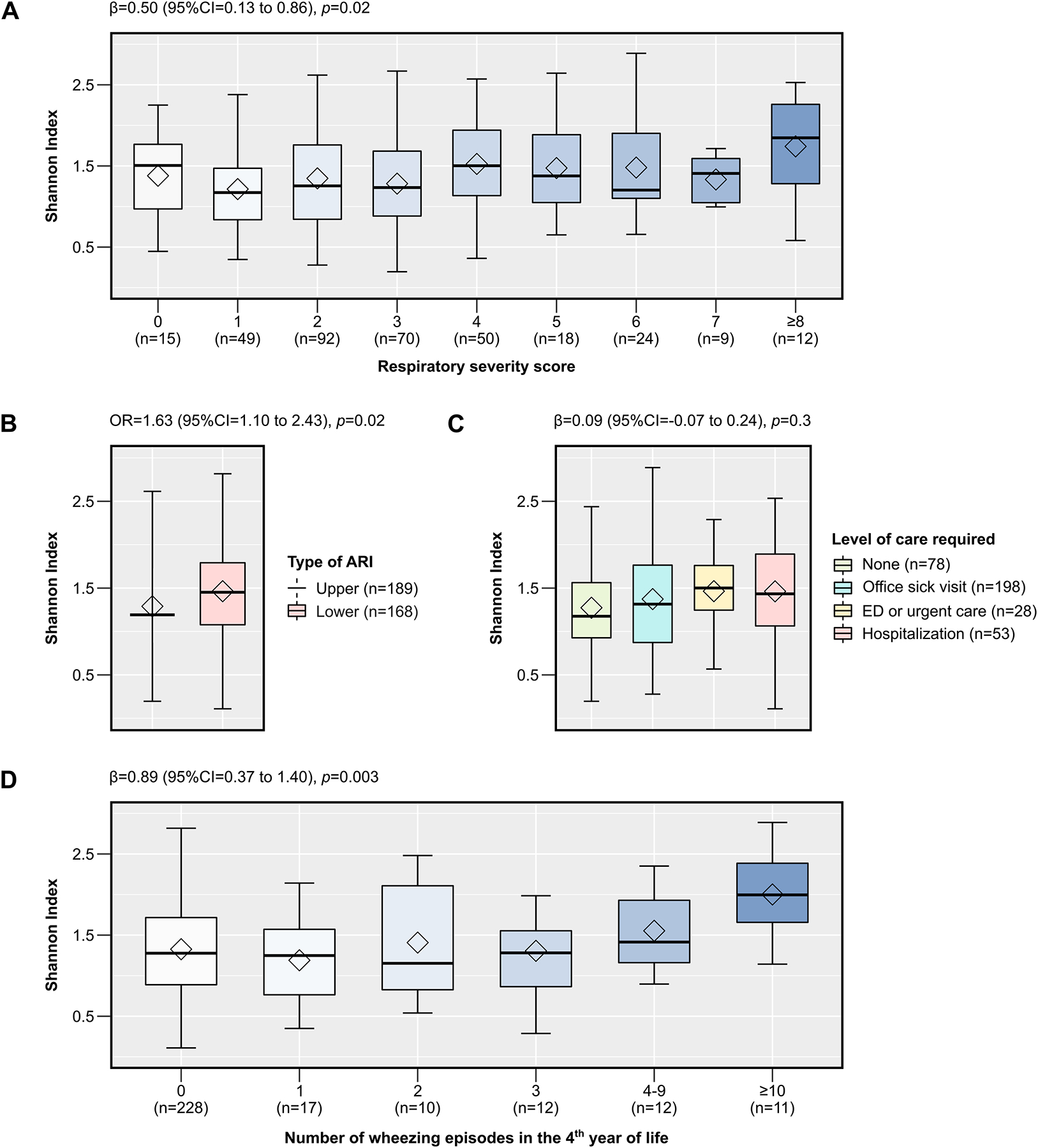
The association of the α-diversity of the upper respiratory tract microbiome during RSV ARI in infancy with short- and long-term clinical outcomes, including the respiratory severity score (A), type of ARI (B), level of care required (C), and number of wheezing episodes in the 4th year of life (D). The box-and-whisker plots show the mean (diamond), median (middle bar), 1st quartile (lower bar), 3rd quartile (upper bar), minimum observation above the lowest fence (lower whisker), and maximum observation below the upper fence (upper whisker) of the Shannon index for each outcome. The total sample size for each outcome (n) and the estimates from corresponding linear or logistic regression models (regression coefficient [β] or OR, 95% CI, and p-value) are also shown, as appropriate. Every model also included infant- and RSV-related covariates (see main text for more details). The Benjamini-Hochberg procedure was used to control for multiple comparisons by adjusting the p-values for the number of clinical outcomes assessed (i.e., controlling for a total of 4 tests). Definition of abbreviations: ARI = Acute respiratory infection, RSV = Respiratory syncytial virus.
