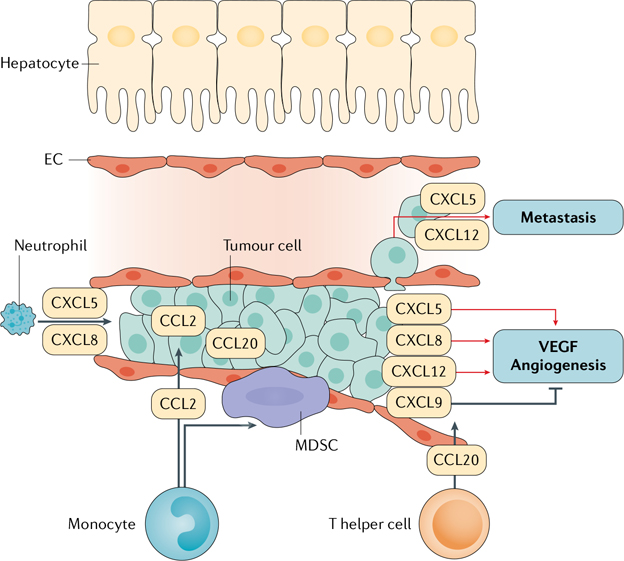
Fig. 3 |. Chemokine actions in HCC.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumour cells produce a large number of chemokines. Among them, CXCL5 and CXCL8 are known to directly stimulate tumour cell growth. They also promote neutrophil infiltration into the liver. CCL2 promotes monocyte recruitment, a subpopulation of which give rise to myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) that suppress the anti-tumour immune response. CCL20 can promote the recruitment of T helper cells. These chemokines also have important roles in angiogenesis: multiple chemokines, such as CXCL5, CXCL8 and CXCL12, promote angiogenesis, whereas CXCL9 suppresses it. CXCL5 and CXCL12 also promote tumour invasion and metastasis. These specific enhancers provide a unique angle with which to study the activation of transcriptional responses to signals such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF) in liver diseases32,41. EC, endothelial cell; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.