Figure 10.
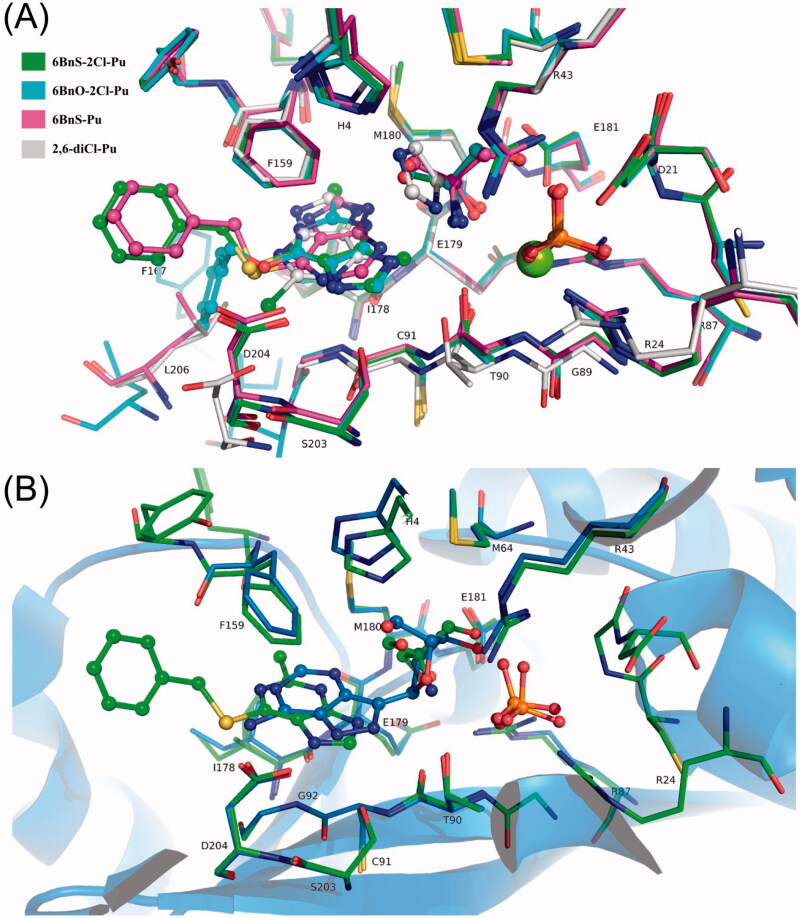
(A) Overlapped positions of ligands in H. pylori PNP complexes with 6BnS-2Cl-Pu, 6BnO-2Cl-Pu, 6BnS-Pu, and 2,6-diCl-Pu. The colour codes of C atoms are shown in the legend, and other atoms have their standard colours. It is visible that the purine ring occupies the base binding pocket. Ligands 6BnS-2Cl-Pu and 6BnO-2Cl-Pu have the plane of the ring almost in the identical position, with the chlorine atoms pointing away from the viewer, although their benzyl arms are positioned oppositely. The pentose binding part of the active site is occupied by Tris molecules in all structures except for imidazole in the structure with 2,6-diCl-Pu. It can be noted that two imidazole nitrogen atoms are positioned close to the positions of one oxygen and one nitrogen atom of Tris molecule to favour hydrogen bond contacts. The phosphate molecules in all structures occupy the same place and are in the same orientation, while in the structure with 2,6-diCl-Pu a highly coordinated Mg atom is located in this position. It is visible that in the structure with 2,6-diCl-Pu the second chlorine atom of the ligand displaces the Asp204 side chain. (B) Overlap of the structure with 6BnS-2Cl-Pu (green) and with formycin A and PO4 (PDB code 6F4X, shown in blue). It can be noted that the base rings are oriented in the same way but are slightly tilted and shifted in relation to each other with formycin A located deeper in the active site because of the covalent bond with the ribose. The molecule of Tris is mimicking the ribose part of formycin A with oxygen atoms occupying similar positions.