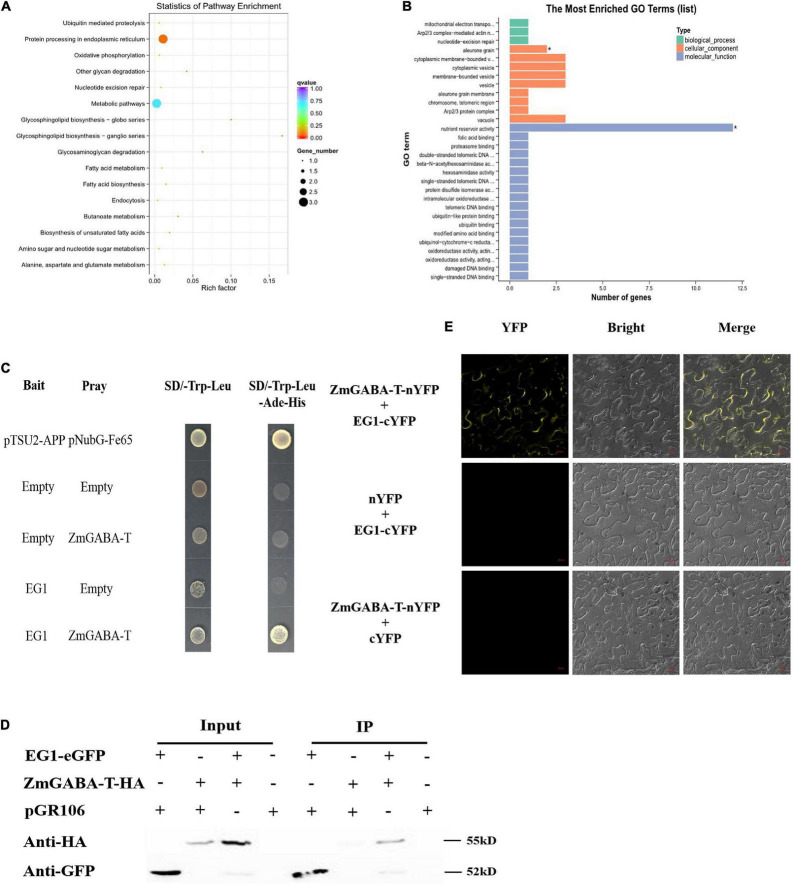
FIGURE 1.
EG1 interacts with ZmGABA-T. (A) Biological function pathways of candidate genes. There are 43 genes in total. And all the 43 genes were classified into 16 types according to their functions: Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis, protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum, oxidative phosphorylation, other glycan degradation, nucleotide excision repair, metabolic pathways, glycosphingolipid biosynthesis–globo series, ganglio series, glycosaminoglycan degradation, fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid biosynthesis, endocytosis, butanoate metabolism, biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, amino sugar, and nucleotide sugar metabolism, and alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism. (B) Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of candidate genes. The function of genes is divided into three parts: Biological process, cellular component, and molecular function. And the genes function of nutrient reservoir activity has the largest number. Enriched P-values less than 0.05 are marked with “*”. (C) Interactions between EG1 with ZmGABA-T in the DUAL membrane yeast 2 hybrid system. Yeast NMY32 cells cotransformed with bait and prey vectors were grown on QDO (SD/–Ade/–His/–Leu/–Trp) medium. The combination of pTSU2-APP and pNubG-Fe65 was used as a positive control, while the combination of pTSU2-APP and pPR3N was used as the negative control. (D) Interactions between EG1 with ZmGABA-T in Nicotiana benthamiana. pGR106 carried EG1-EGFP and ZmGABA-T-HA, respectively, were coexpressed in Nicotiana benthamiana. Around 48 h after infiltration, immunoprecipitates obtained from whole-cell extracts using anti-GFP trap beads were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-GFP antibodies. This experiment was repeated three times with the same results. (E) BiFC assay in Nicotiana benthamiana. Bars = 20 μm.