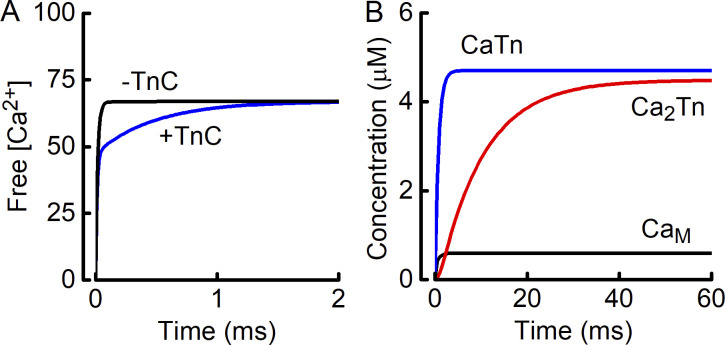
Figure A2.
Analysis of Ca binding by TnC. (A) Computed time course of establishment of equilibrium between Ca2+ and EGTA. At time 0, all Ca2+ bound to EGTA. The kinetic model was used to compute the change in unbound Ca2+. The effects of including TnC (labeled +TnC) or considering EGTA alone (−TnC) are shown. In the presence of TnC, equilibration of Ca2+–EGTA takes longer (~2 ms), but the eventual free [Ca2+] level (67 nM) is the same whether TnC is included or not. (B) Calculated time courses of Ca2+ binding by TnC. First Ca2+ binds rapidly (blue) and second Ca2+ (red) more slowly. Unbound [Ca2+] attains a steady value (600 nM in this example) more rapidly than CaTn, reflecting the binding kinetics of EGTA. EGTA effectively buffers Ca2+ even when Ca2+ is being bound by TnC.