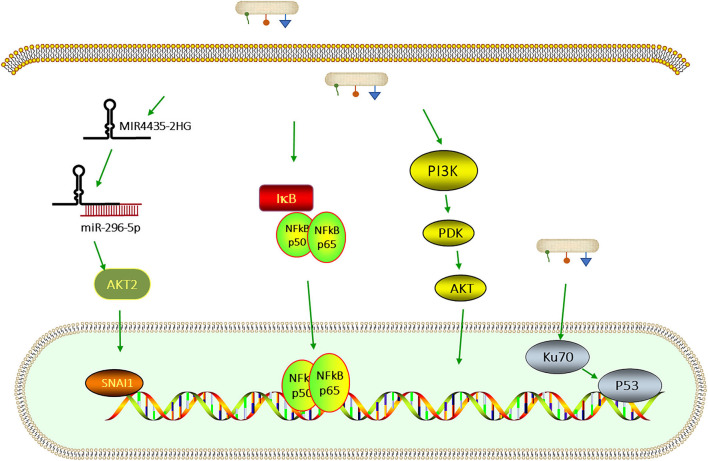
Figure 2.
Signaling pathways that are related to F. nucleatum infection. F. nucleatum upregulates MIR4435-2HG, which binds miR-296-5p and weakens the inhibitory effect of miR-296-5p on SNAI1 via AKT2 [77]. F. nucleatum can also activate the PI3K/AKT—nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway which regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and the inflammatory response [72]. The infection with F. nucleatum promotes the capability of proliferation by leading to DNA damage through the Ku70/p53 pathway [78].