Figure 6.
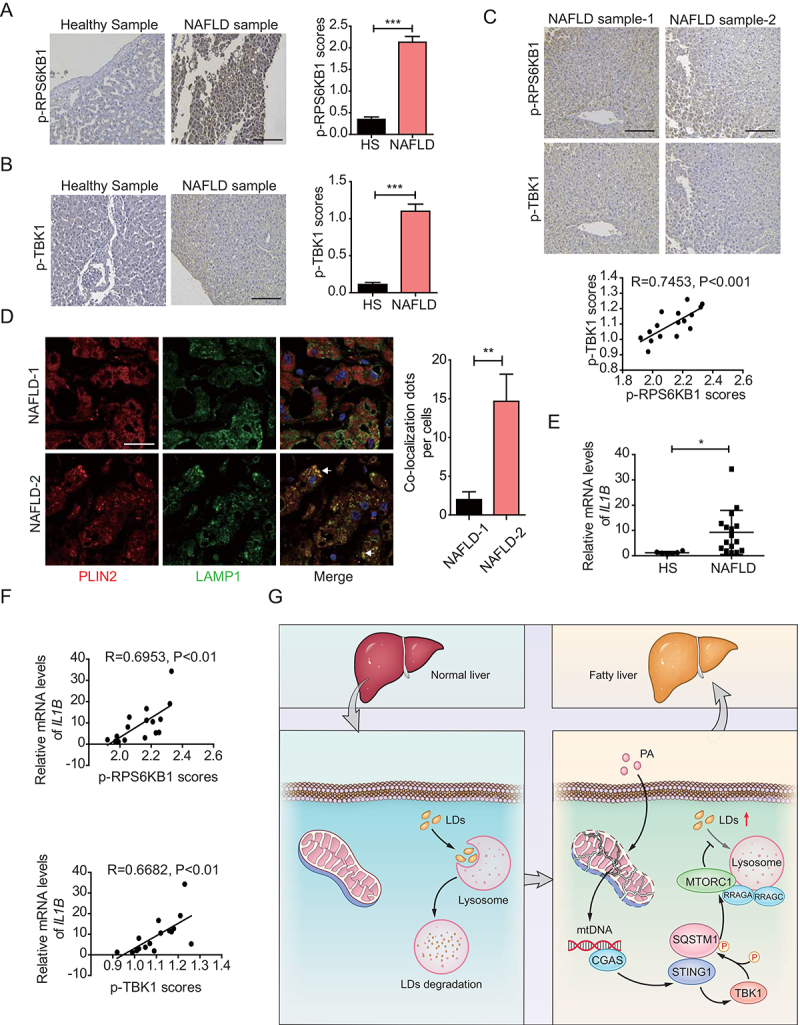
Concomitant enhancement of phosphorylated levels of RPS6KB1 and TBK1 correlates with inflammatory levels in liver tissues with NAFLD. (A) Immunohistochemical staining of 6 cases of normal human liver tissue specimens (Healthy Sample, HS) and 16 cases of NAFLD specimens (NAFLD Sample, NAFLD) with the anti-p-RPS6KB1 antibody. Scale bar: 100 μm. Quantitative analysis of p-RPS6KB1 staining is shown as scores. The data are presented as means ± SD. ***p < 0.001. (B) Immunohistochemical staining of normal human liver tissue specimens (Healthy Sample, HS) and NAFLD specimens (NAFLD Sample, NAFLD) with the anti-p-TBK1 antibody. Scale bar: 100 μm. Quantitative analysis of p-TBK1 staining is shown as scores. The data are presented as means ± SD. ***p < 0.001. (C) Human NAFLD specimens were immunohistochemically stained with anti-p-RPS6KB1 or anti-p-TBK1 antibodies. Representative images are shown. Scale bar: 100 μm. The correlation of p-RPS6KB1 and p-TBK1 was statistically significant among different specimens (n = 16, r = 0.7435, p < 0.001). (D) Confocal microscopy of human NAFLD specimens using in above. NAFLD-1 is related to the NAFLD sample-1 in (C). NAFLD-2 is related to the NAFLD sample-2 in (C). Representative images are shown. Scale bar: 10 μm. The quantitative data are presented as means ± SD. **p < 0.01. (E) The IL1B mRNA expression level in the normal liver (healthy sample, HS) (n = 6) and NAFLD tissue (NAFLD) (n = 16) samples was determined by qPCR assay. The data are presented as means ± SD. *p < 0.05. (F) The correlation of IL1B mRNA expression and p-RPS6KB1 (upper) and p-TBK1 (lower) was statistically significant among different specimens (n = 16). (G) Schematic representation of STING1-regulated MTORC1 activity and lipophagy under PA treatment.
