Figure 1 |. Proposed mechanisms of injury induced by retinoic acid receptor responder protein 1 (RARRES1) in glomerular cells through autocrine and/or paracrine pathways.
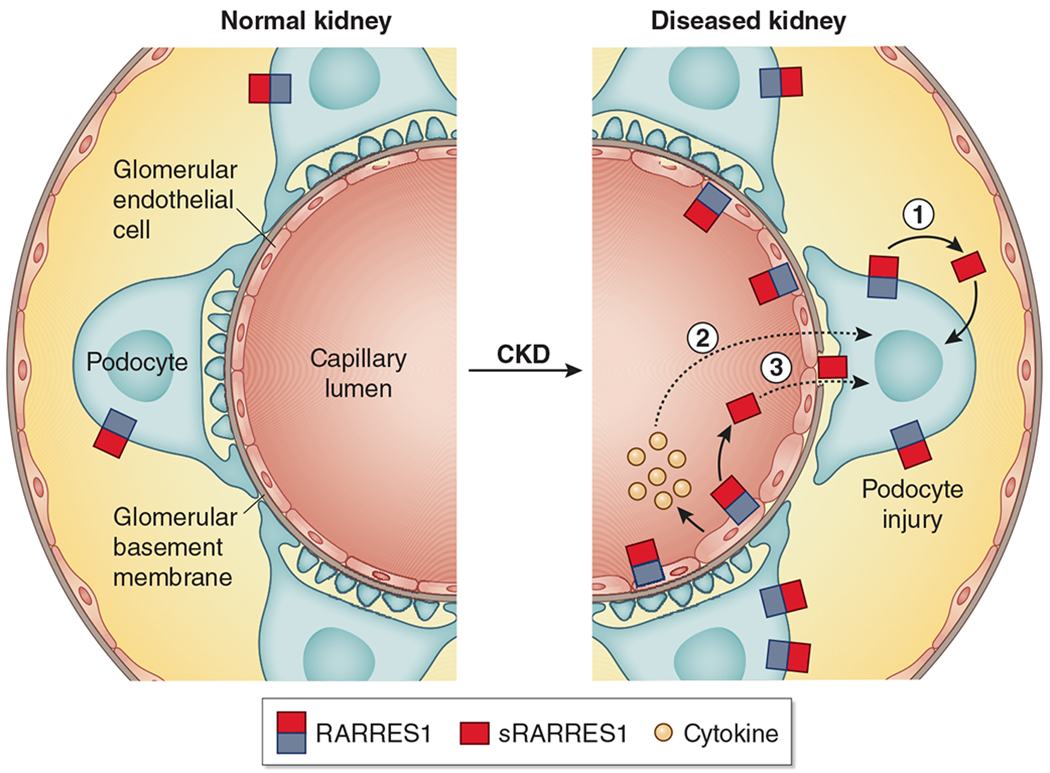
In normal kidneys, RARRES1 is expressed specifically in podocytes. In diseased kidneys, RARRES1 expression is significantly increased in podocytes, which can be cleaved into its soluble form and endocytosed by podocytes, leading to podocyte apoptosis (1); RARRES1 expression is also found to be increased in endothelial cells to promote podocyte injury through an endothelial–podocyte crosstalk, probably via cytokine released by injured endothelial cells (2) or by podocyte uptake of soluble RARRES1 (sRARRES1) generated from the endothelial cells (3). CKD, chronic kidney disease.
