Figure 4. Genetic variants with islet cell type- and state-specific effects on chromatin accessibility.
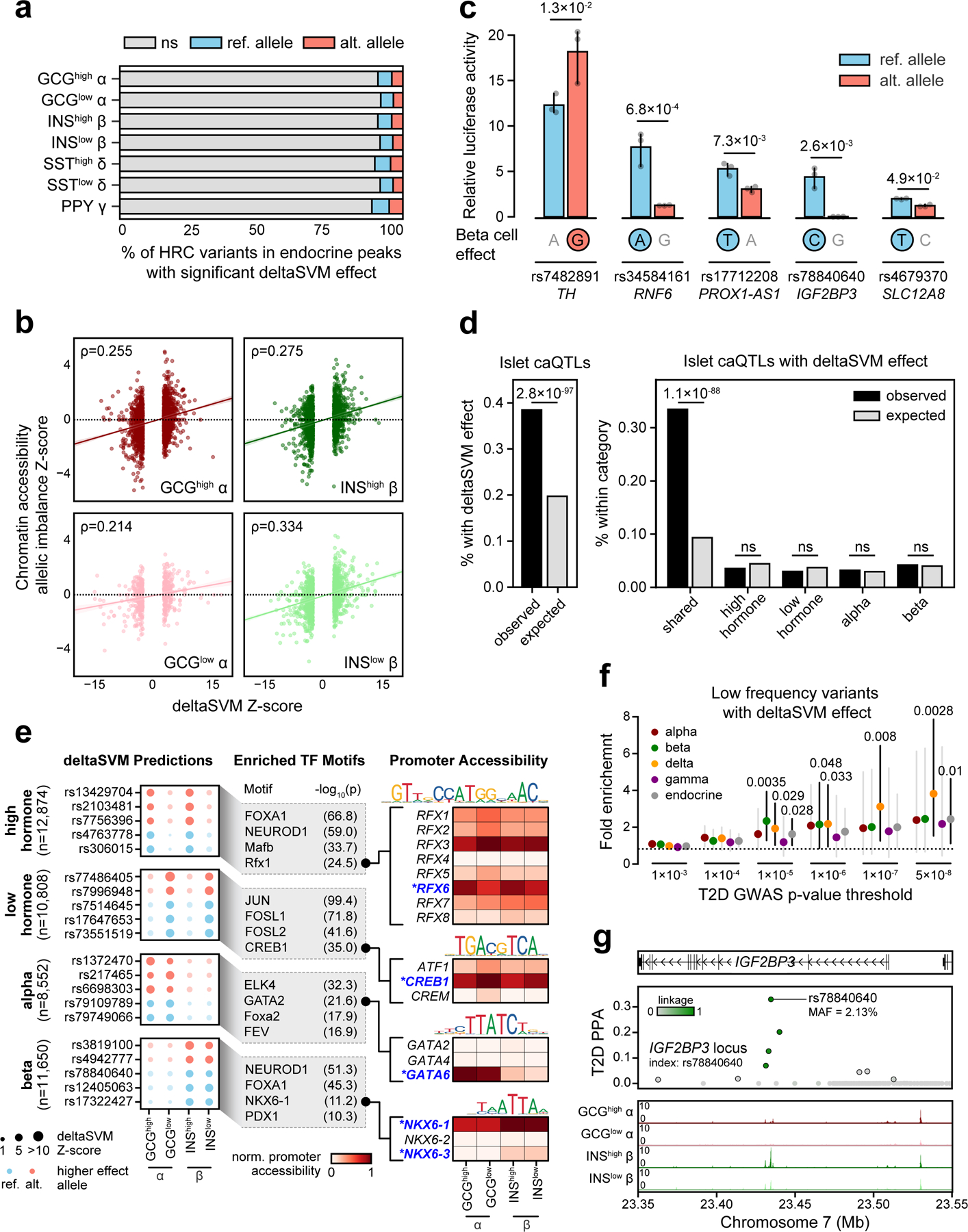
(a) Percentage of HRC variants in any endocrine cell type peak (n=1,411,387 variants) that had significant deltaSVM effects (FDR<0.1) for the reference (ref.) or alternative (alt.) allele. (b) Spearman correlation between deltaSVM Z-score and chromatin accessibility allelic imbalance Z-scores for variants with predicted effects in alpha and beta states. (c) Relative luciferase reporter activity (mean ± 95% CI; n=3 replicates) for five T2D variants with predicted beta cell effects. The allele with predicted effect is circled. p-values by two-sided Student’s T-tests. (d) Enrichment of islet caQTLs for variants with predicted effects in alpha and beta cells (left) and stratified based on shared, cell type- and state-specific effects (right). p-values by two-sided Fisher’s exact test, ns, not significant. (e) Examples of variants with predicted effects in alpha and beta cells (left). TF motif families enriched in sequences surrounding the effect allele relative to the non-effect allele (middle). Promoter accessibility patterns for genes in enriched TF motif families (right). Genes with matching promoter accessibility and TF motif enrichment patterns are highlighted. (f) Enrichment (estimate ± 95% CI) of low frequency and rare variants with predicted effects on islet chromatin at different T2D association thresholds. p-values by two-sided binomial test. (g) Low-frequency T2D variant rs78840640 at the IGF2BP3 locus with high causal probability (PPA=0.33) has predicted effects in beta cells.
