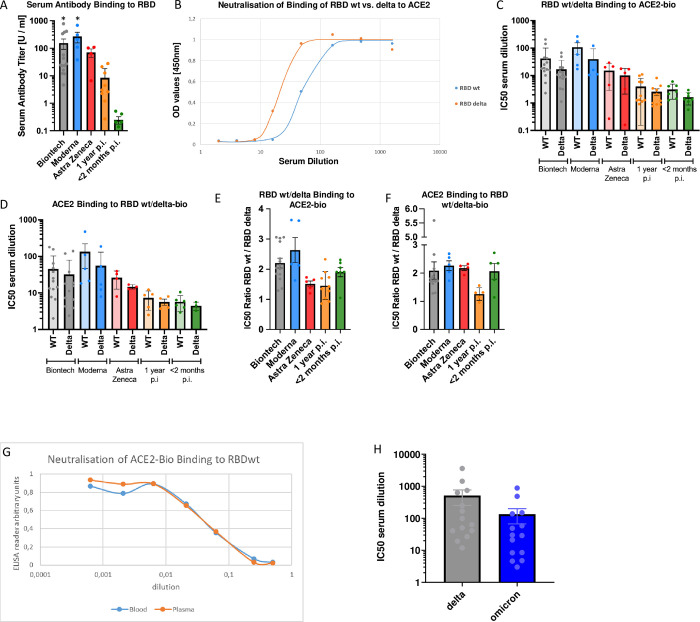
Fig 2. Serum antibodies and neutralisation.
The bar graphs show results of n = 13 independent individuals after vaccination with BioNtech (grey), n = 5 Moderna (blue), n = 5 AstraZeneca (red), and n = 10 independent individuals one year (orange), and n = 7 subjects < 2 months (green) after natural infection with standard errors of the mean (SEM). Significance was tested by one-way ANOVA (A) or by Kruskal-Wallis test for non-parametric values (B–E). **p < 0.05 vs. naturally infected subjects. A: Anti RBD antibody titres; B: Representative curve of a single experiment to determine IC50-values for the inhibition of biotinylated ACE2 binding to immobilized wt vs. delta mutant RBD. C: Absolute IC50-values calculated for the inhibition of biotinylated ACE2 binding to immobilized wt vs. delta mutant RBD. D: Absolute IC50-values calculated for the inhibition of biotinylated wt vs. delta mutant RBD binding to immobilized ACE2. E: Ratios between IC50-values calculated for inhibition of ACE2 binding to immobilized wt vs. delta mutant RBD. F: Ratios between IC50-values calculated for inhibition of wt vs. delta mutant RBD binding to immobilized ACE2. G: Read-out of a representative experiment showing the comparison between inhibition of biotinylated ACE2 binding to immobilized RBD with serum taken by venous sampling vs a drop of full blood. H: In additional, independent group of 14 subjects who had been fully vaccinated with BNT 162b2, we also investigated ratios between IC50 values calculated for inhibition of ACE2 binding to immobilized omicron vs. delta mutant RBD.