Fig. 7 |. Key limitations of nucleic acid-based nanoparticle clinical translation and potential strategies to tackle their limitations.
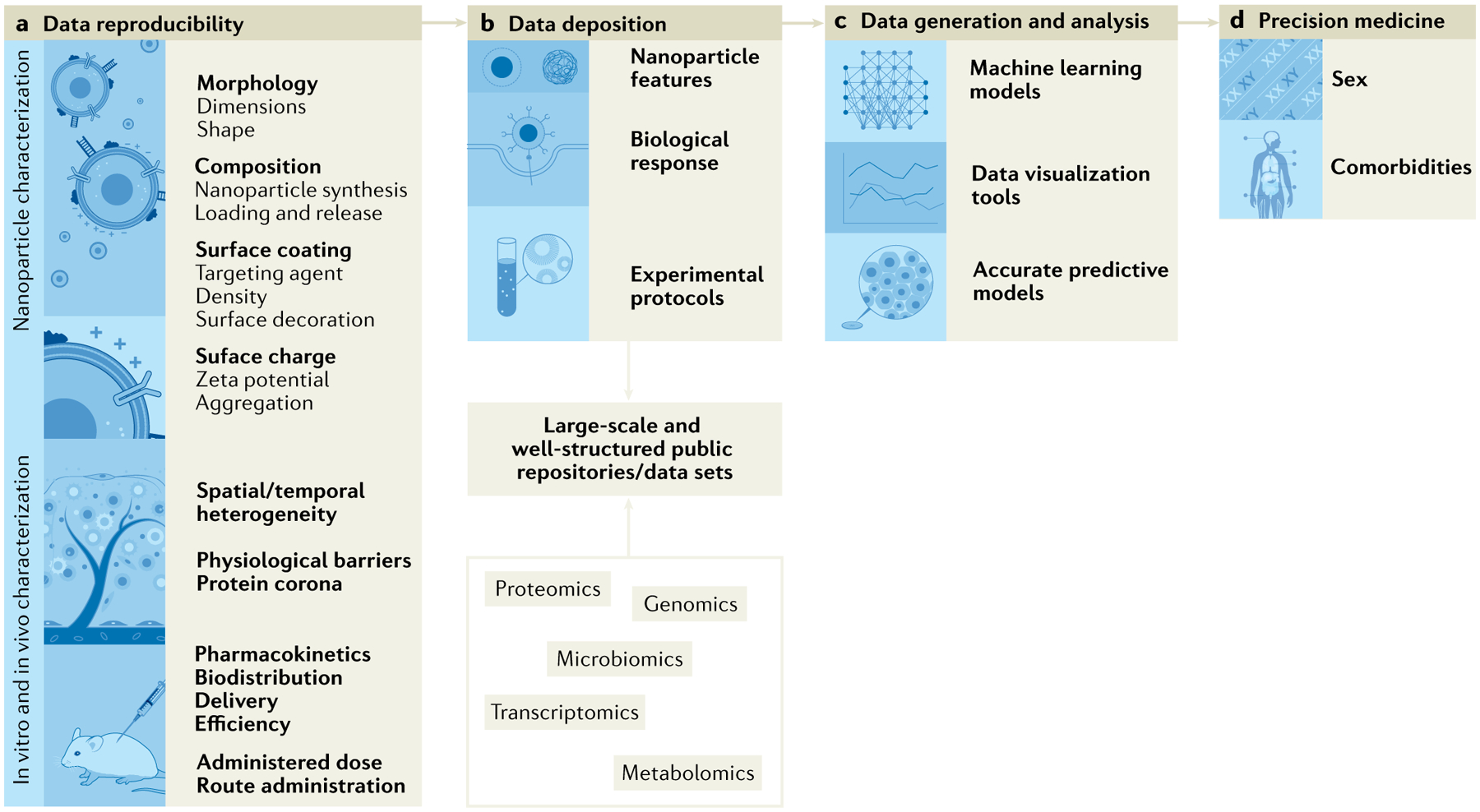
a | Scientific community efforts focus on the importance of standardized nanoparticles and bio–nano interface characterization, and their impact on data reproducibility111. b | Development of large-scale and well-structured repositories is challenging owing to the broad procedures, terms, abbreviations and acronyms of the scientific field111. c | Machine learning will allow generation of predictable models for in silico nanoparticle design taking into account physico-chemical properties (size, zeta potential) and their in vitro and in vivo response47,205. d | Nanoparticle design is envisioned to focus on precision medicine therapies, instead of one-size-fits-all strategies44.
