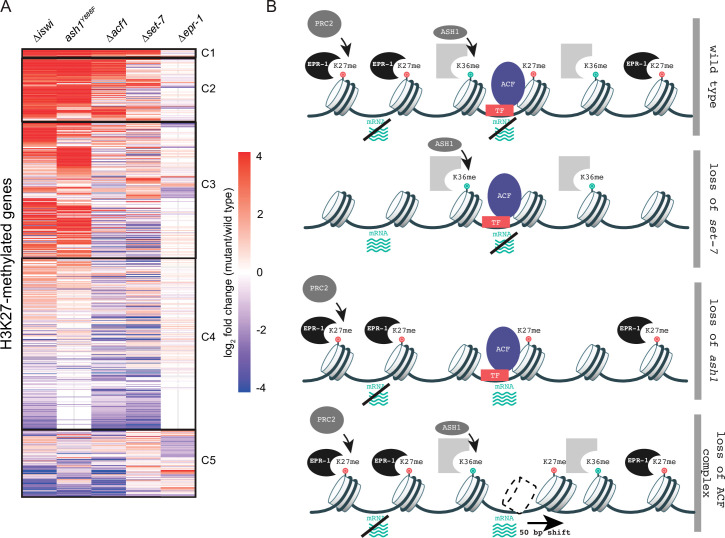
Figure 6. Multifaceted repression in facultative heterochromatin.
(A) Clustered heatmap made using mRNA-seq data for combined biological replicates of the indicated mutant strains. All H3K27-methylated genes that had reads in mRNA-seq data were included (n=821). Clusters (C1–C5) were determined by eye. (B) Model depicting our current framework of factors responsible for maintaining gene silencing in regions marked by H3K27 methylation. Loss of this methyl-mark itself is sufficient to activate a fraction of genes, in part because of loss of the H3K27 methyl-specific factor EPR-1. Repression of many other genes, in H3K27-methylated domains and elsewhere, depend on both H3K36 methylation by ASH1 and both components of the ACF complex (ISWI and ACF). Gray partial square represents an unknown H3K36 methyl binding protein. TF represents unknown transcription factor(s) that could recruit/direct the ACF complex.
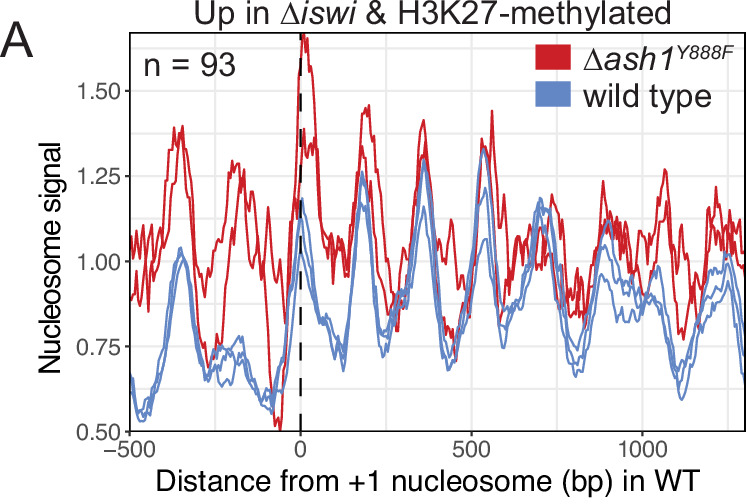
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Loss of ash1 function does not result in a downstream nucleosome shift.