Figure 1. Clinical presentation of warts on the backs of hands of patients with cutaneous HPV infections and identification of HPV types by whole transcriptome sequencing.
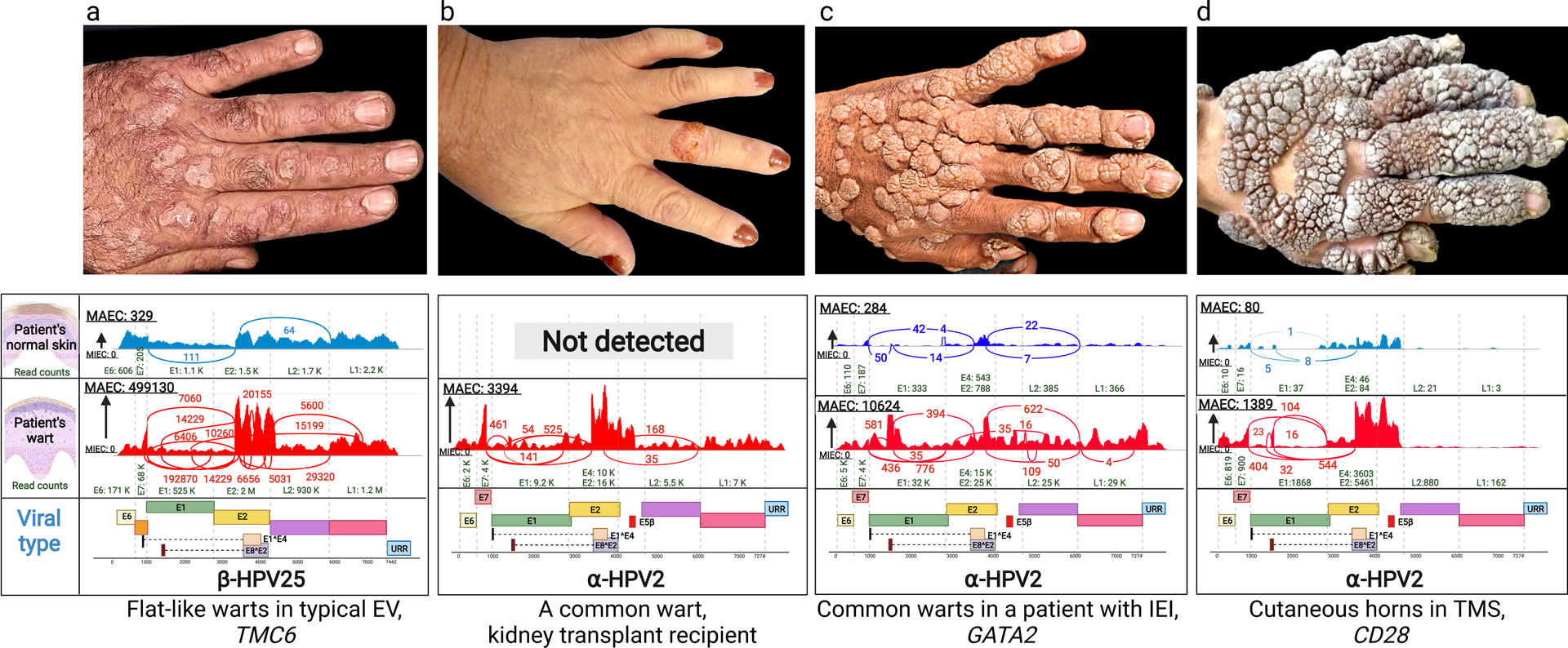
(a) Multiple flat warts in a patient with typical EV caused by mutations in the TMC6 gene. (b) A solitary common wart in the middle finger of a kidney transplant patient. (c) Multiple common warts in a patient with primary inborn error of immunity (IEI) caused by mutations in GATA2. (d) Exophytic warts and cutaneous horns in a patient with TMS due to mutations in CD28. Below each clinical picture, there are representative Sashimi plots derived from whole transcriptome sequencing by RNA-Seq, identifying the types of HPV associated with the lesions shown above or in the normal appearing skin of the same patients. The corresponding genomic structures of HPVs are shown below; note the presence of Early (E1–8), Late (L1 and L2) and Upstream Regulatory Region. The copy number of viruses is very low (a, c and d), or completely absent (b), in normal appearing skin adjacent to the warts. HPV, human papilloma virus; EV, epidermodysplasia verruciformis; IEI, inborn error of immunity; MAEC, Maximum exon coverage; MIEC, Minimum exon coverage; TMS, the tree-man syndrome.
