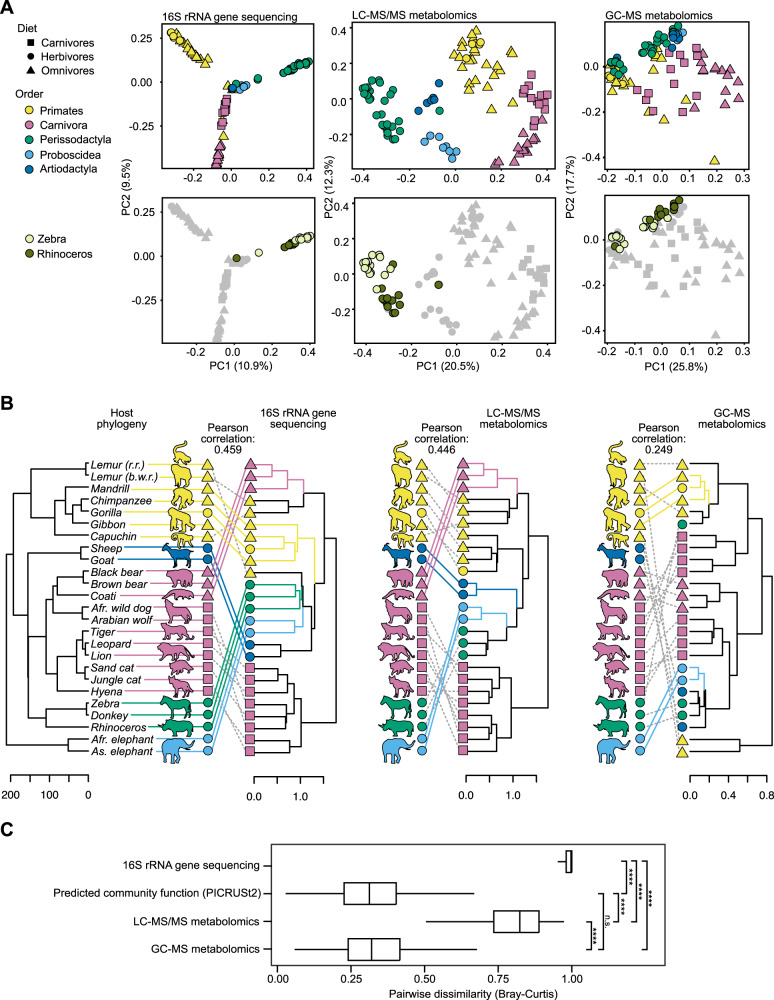
Fig. 1. Mammalian metabolomes mirror microbiomes, reflecting functional richness across host species.
A Top, Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of samples based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity for the microbial composition (16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing), LC–MS/MS metabolome and GC–MS metabolome. Bottom, PCoA analysis with zebras and rhinoceroses highlighted. B Comparison of the phylogenetic tree of the mammalian host species to the hierarchical clustering tree of samples for each data type, based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. Solid, colored lines connect subtrees that match in both trees. C Comparison of the degree of dissimilarity between samples in different data types using Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. For the boxplots, the lower and upper hinges correspond to the first and third quartiles, and outliers are not shown. The significance was determined using one-way ANOVA analysis followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test, resulting in adjusted p values noted as follows: p > 0.05 = n.s., p < 0.0001 = ****.