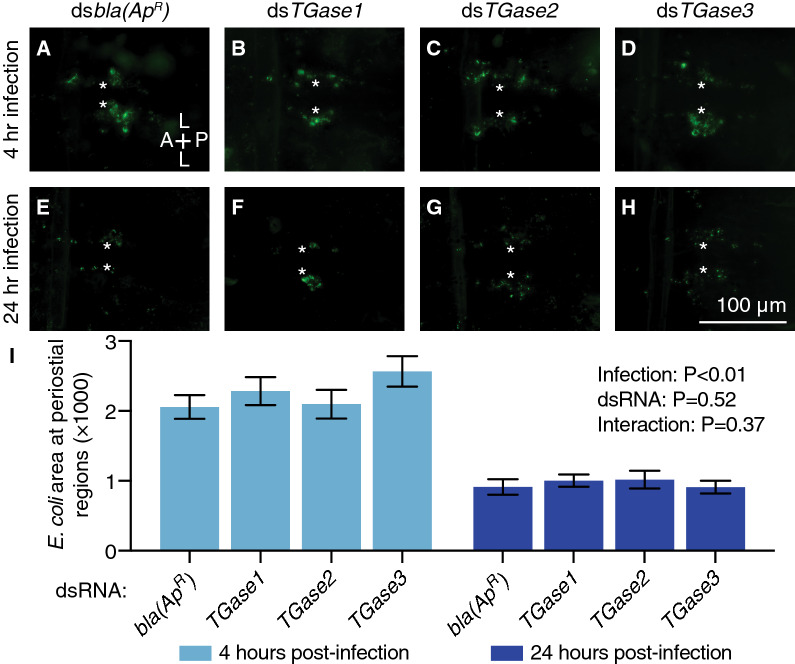
Figure 4.
RNAi-based knockdown of transglutaminase genes does not alter the accumulation of GFP-E. coli in the periostial regions. (A–H) Fluorescence images show a single abdominal segment with phagocytosed bacteria (green) surrounding the ostia (asterisks) in mosquitoes that had been infected with GFP-E. coli for 4 (A–D) or 24 h (E–H). Prior to treatment, mosquitoes had been injected with dsbla(ApR) (A, E), dsTGase1 (B, F), dsTGase2 (C, G) or dsTGase3 (D, H). A, anterior; P, posterior; L, lateral. (I) Graph shows the average area of GFP-E. coli in dsbla(ApR)-, dsTGase1-, dsTGase2- and dsTGase3-injected mosquitoes that had been infected with GFP-E. coli for 4 or 24 h. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, using dsbla(ApR) mosquitoes as the reference. Column heights mark the means, and whiskers show the S.E.M.