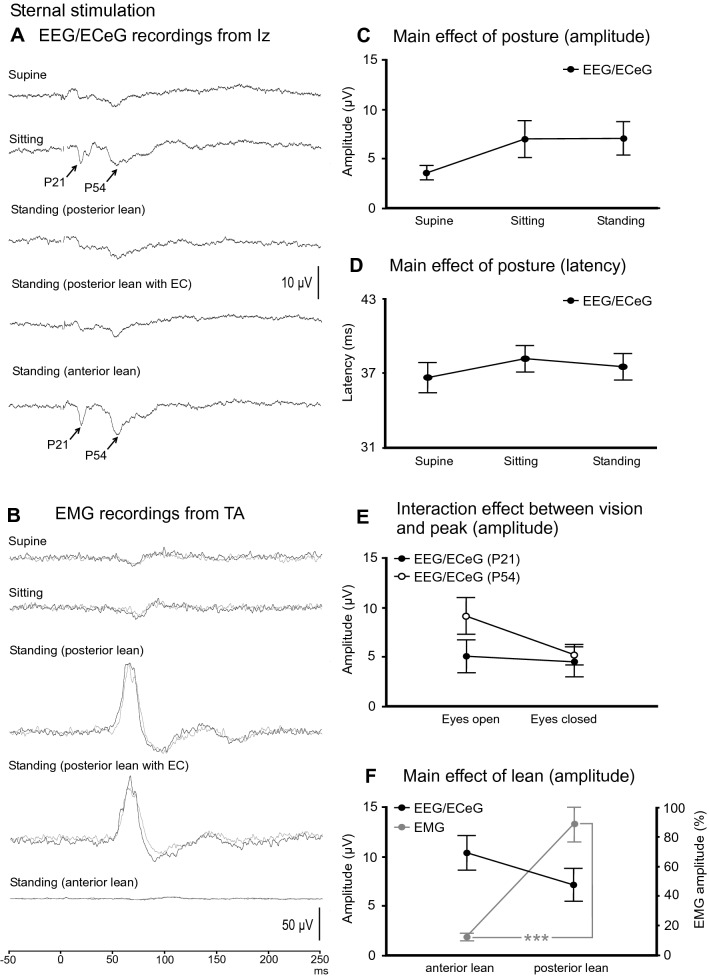
Fig. 7.
A Grand mean recordings from Iz during sternal stimulation show the P21 and P54 peaks to be less prominent and not well formed across the conditions tested. The evoked EMG response in tibialis anterior (TA) was attenuated in the supine and sitting conditions as well as during standing with anterior lean, which does not pose a threat to postural stability. The evoked response at Iz tended to be smaller in the supine position (C) while latency was unaffected by posture (D). The P54 peak was more affected by vision than the P21 peak, with smaller amplitudes during eye closure (E). Anterior lean tended to produce larger EEG/ECeG responses than posterior lean whereas EMG responses were significantly larger during posterior lean (F). Baseline rectified EMG levels for TA were 69.1 (supine), 82.4 (sitting), 73.8, 64.8 (standing, posterior lean, eyes open and closed) and 11.2 µV (standing, anterior lean). ***P < 0.001