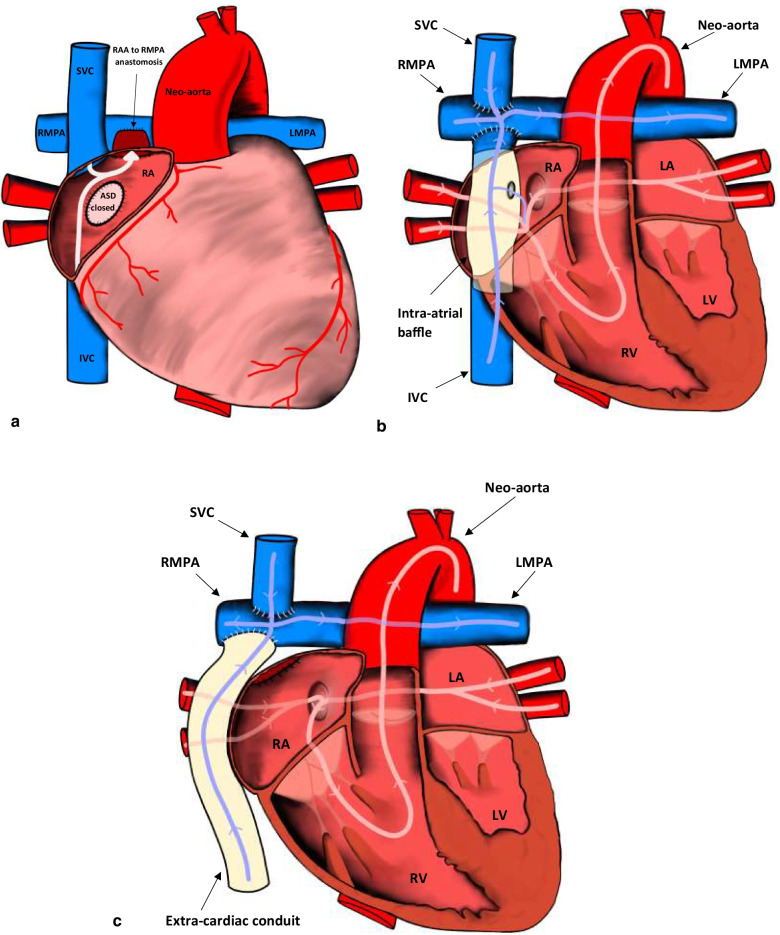
Fig. 7.
a The last and final stage (Stage 3) for definitive repair of single ventricle defects. The IVC is connected to the RMPA to form the atriopulmonary variation of the Fontan procedure. The ASD is closed, and the RAA is anastomosed to the RMPA. ASD: atrial septal defect; IVC: inferior vena cava; LMPA: left main pulmonary artery; RAA: right atrial appendage; RMPA: right main pulmonary artery; RA: right atrium; SVC: superior vena cava. b The lateral intracardiac tunnel variation of the total cavopulmonary connection Fontan procedure. A baffle is placed inside the RA, and the SVC is connected directly to the RMPA. A fenestration to relieve pressure in the circuit may be seen between the baffle and the RA. IVC: inferior vena cava; LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle; LMPA: left main pulmonary artery; RMPA: right main pulmonary artery; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle; SVC: superior vena cava. c The extracardiac conduit variation of the total cavopulmonary connection Fontan procedure. Note that the conduit that directs venous blood to the RMPA is extracardiac as opposed to the lateral intracardiac tunnel variation. LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle; LMPA: left main pulmonary artery; RMPA: right main pulmonary artery; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle; SVC: superior vena cava