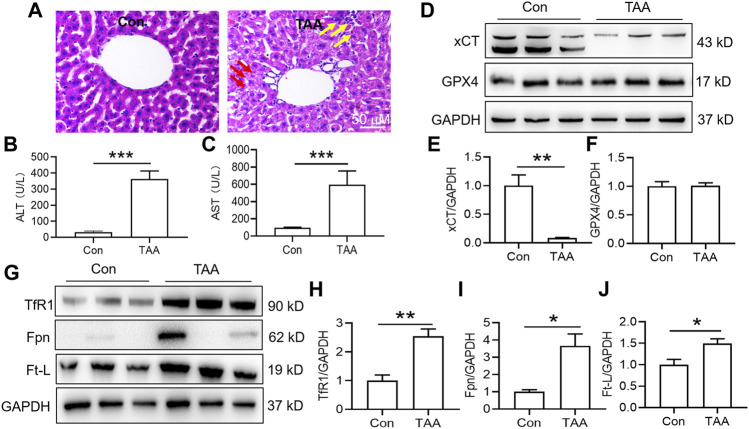
FIGURE 1.
TAA induced liver dysfunction, suppressed anti-ferroptosis-related protein expression and enhanced iron-related protein expression in the liver. (A) Liver injury was assessed by H&E staining and histological examination in mice with or without TAA administration for 3 days (bar = 50 μm). TAA induced prominent inflammation (yellow arrow) and vacuolar degeneration (red arrow) in the liver within 3 days compared with the control group. (B) Plasma ALT and (C) AST levels in control and TAA-injected mice. (D) Western blotting analysis of xCT and GPX4 expression in the livers of mice with or without TAA treatment. (E–F) Relative protein expression levels of xCT and GPX4. (G) Western blotting analysis of TfR1, Fpn and Ft-L expression in the livers of mice with or without TAA treatment. (H–J) Relative protein expression levels of TfR1, Fpn and Ft-L. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 6-9 mice per group); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 versus the indicated group.