Fig. 4.
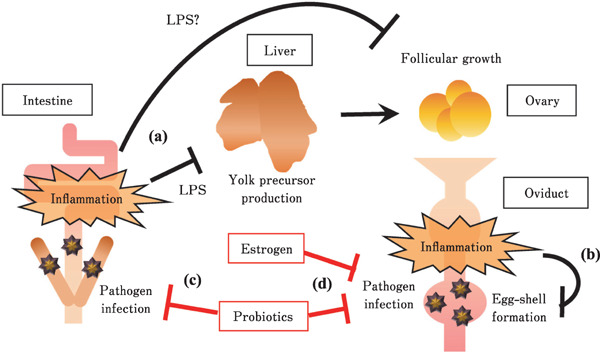
Representative diagram describing the effects of inflammation condition and enhancement of mucosal barrier function in the intestine and oviduct on egg production of laying hens. (a) Intestinal inflammation caused by pathogen infection leads disruption of liver function through influx of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and disorder of follicular growth. LPS probably directly disrupts the function of follicular growth in the ovary. (b) Inflammation in oviduct causes disorder of egg-shell formation. These inflammation in both intestine and oviduct leads disorder of egg production. (c) Probiotics enhances mucosal barrier function in the intestine, it may be following prevention of liver and ovarian functional disorder caused by disruption of intestinal mucosal barrier function. (d) Estrogen and proper antigen stimulation such as probiotics stimulation enhance mucosal barrier function in the oviduct. The enhancement of barrier function in both intestine and ovary may contribute to improvement of egg production.
