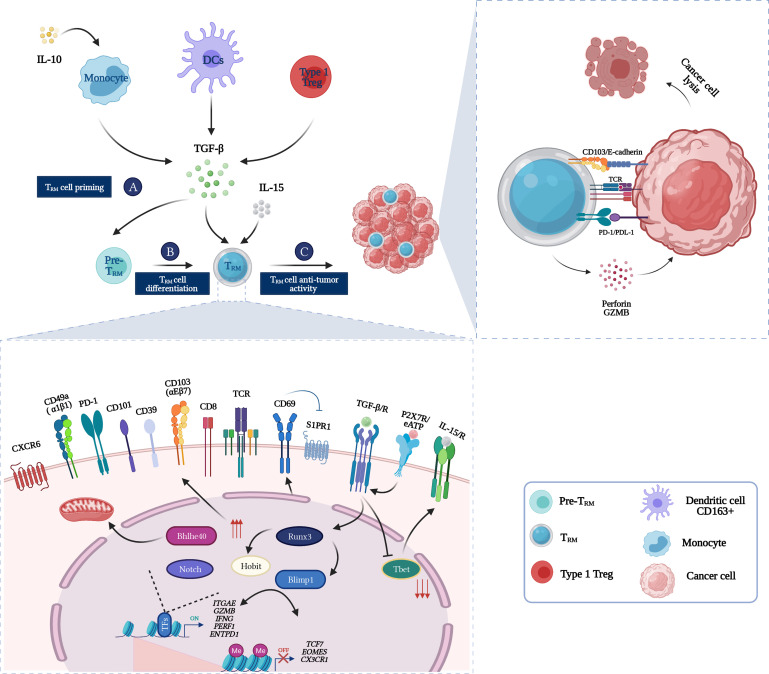
Figure 3.
From Zero to Hero: TRM cells in the cancer-immunity cycle. (A) TRM cells precursors are primed in the tumor-draining lymph node by DCs. (B) Once in the tumor microenvironment and in the presence of TGF-β and IL-15, TRM cells precursors will differentiate into TRM cells. Induction of a core residency signature such as expression of tissue retention molecules (CD103, CD69, CD49a, CXCR6) and acquisition of high cytotoxic activity (GZMB, perforin) is under epigenetic regulation and key transcription factors instructions (Blimp1, Hobit, Runx3, Bhlhe40, and Notch). (C) Once fully differentiated, tumor-specific TRM cells can enact cancer cells eradication via an arsenal of cytotoxic molecules such as perforin and granzyme. CD103 expression enables TRM cells biding to E-cadherin expressing tumor cells which sustains the immunological synapse, hence triggering lytic granules polarization and exocytosis. DC, dendritic cell; TRM, tissue-resident memory T cells.