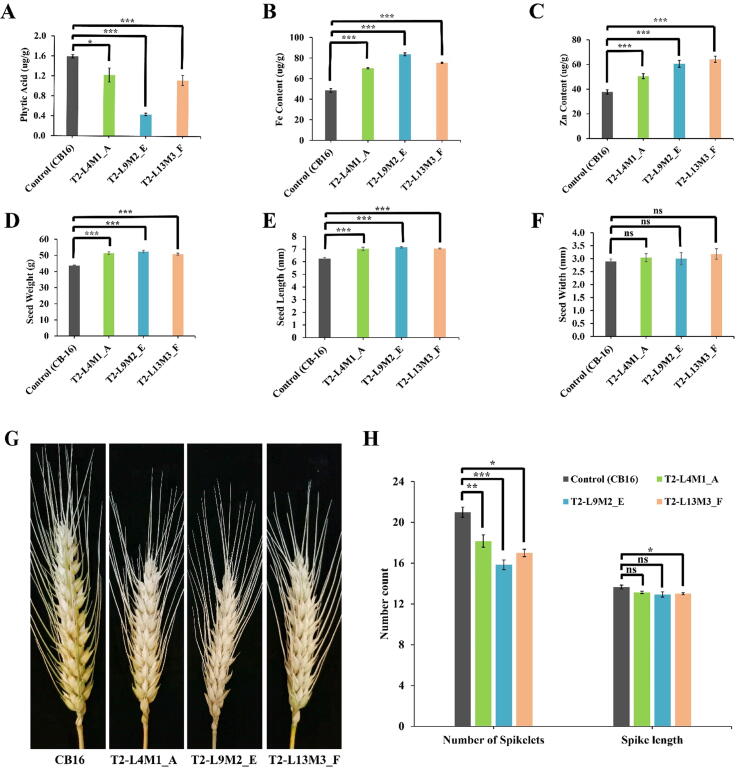
Fig. 5.
Micronutrient and phenotypic analysis of the mature T2 grains of genome edited mutant lines. (A) Total Phytic acid (PA) in the mature T2 seeds of genome edited (GE) mutant lines. PA was measured in the mature T2 seeds from the primary tiller of each GE mutant line. (B, C) Fe and Zn concentration (μg/g) was estimated by using Atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS). (D) Seed weight of control (CB-16) and GE mutant lines. (E) Seed length of control (CB-16) and GE mutant lines. (F) Seed width of control (CB-16) and GE mutant lines. (G) Representative picture of spikes of wheat GE mutant lines and control (scale bar = 1.5 cm). (H) Spike length (cm) and spikelet count from the primary tiller of GE mutant lines and control CB16 at T2 stage. The data indicates the mean ± SE of six biological replicates. Student’s t-test was used to compare the significant variation between each transgenic line and control. *,** and *** shows statistical significance at P < 0.05, P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively, and ns = non-significant.