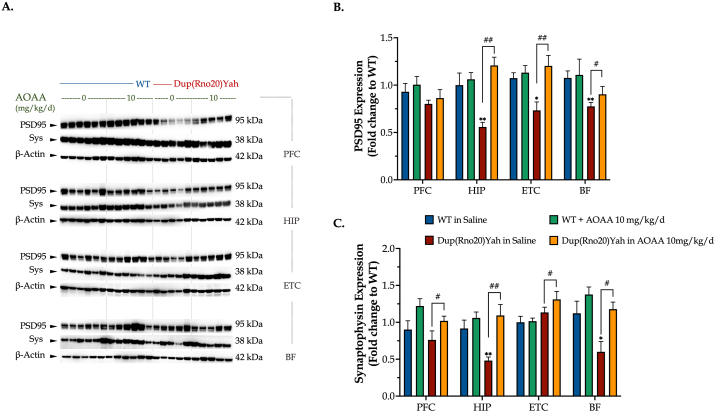
Fig. 12.
DS impairs synaptic protein expression in the brain; restoration by CBS inhibition. Following the cognitive assessment, animals were euthanized and tissue from the prefrontal cortex (PFC), hippocampus (HIP), entorhinal cortex (ETC), and the basal forebrain (BF) brain regions were collected for protein extraction. Protein samples were processed for immunoblotting detection of (A, B) the post-synaptic density protein 95 (PSD95) and (A, C) synaptophysin (Sys). The expression β-actin served as a loading control. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM of 6 animals per experimental condition, except for saline-treated DS where data were expressed as mean ± SEM of 5 animals. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison t-tests at each brain region of interest. *p≤0.05 or **p≤0.01 shows significant differences between saline-treated DS rats and saline-treated WT rats; #p≤0.05 or ##p≤0.01 shows significant effect of AOAA treatment in Dup(Rno20)Yah rats, indicative of restoration of synaptic protein expression.