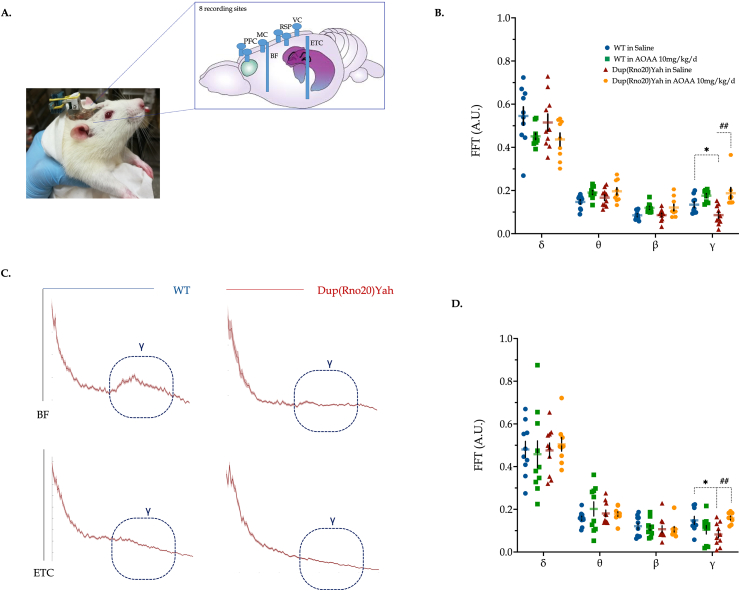
Fig. 13.
DS impairs electrical wave patterns in the rat brain; restoration by CBS inhibition. (A) Representative image for the connectors on the head of rats, along with the differential position of microelectrodes across the brain. Recordings of the brain activity were taken from freely moving animals during behavioral testing in the open field arena. Power spectra were calculated for each epoch by fast Fourier transform; γ activity was calculated by taking the mean value of the power spectrum between 30 and 80 Hz in (B) basal forebrain (BF) and (D) entorhinal cortex (ETC). (C): Representative spectra highlighted with the γ oscillations from the BF and ETC regions of WT and Dup(Rno20)Yah rats. Each point represents one animal. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison t-tests at each brain region of interest. *p≤0.05 shows significant differences between saline-treated DS rats and saline-treated WT rats; ##p≤0.01 shows significant effect of AOAA treatment in Dup(Rno20)Yah rats, indicative of normalization of brain wave patterns.