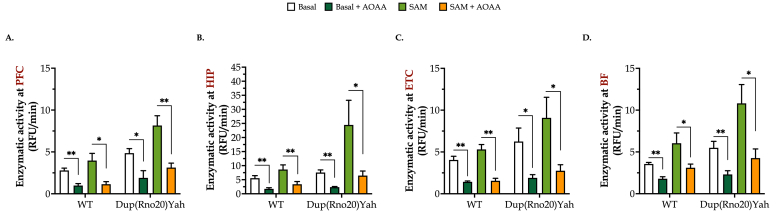
Fig. 5.
DS brain tissues produce more H2S than control tissues in a region-specific manner. Brains from control or Dup(Rno20)Yah rats were dissected into coronal sections of 1 mm, and the regions of (A) the prefrontal cortex (PFC), (B) hippocampus (HIP), (C) entorhinal cortex (ETC), and (D) basal forebrain (BF) were isolated. They were treated with 0 or 100 μM AOAA for 1h at 37 °C and homogenized. Samples were followingly incubated with cysteine and homocysteine in the presence or absence of the allosteric CBS activator S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). Maximally stimulated enzymatic H2S generation, which estimates the maximal capacity of the tissue to produce H2S (rather than basal levels of H2S in the absence of exogenous substrates, which produce low and barely detectable levels in this assay) was measured by following the increase of fluorescence of the AzMC probe over time. Data, expressed as mean ± SEM of 6 animals per experimental condition, were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison t-tests. *p ≤ 0.05 and **p ≤ 0.01 indicate the inhibitory effect AOAA on H2S generation.