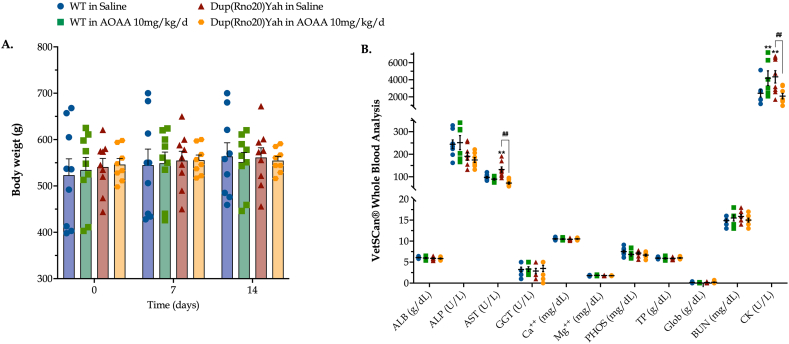
Fig. 7.
Effect of the CBS inhibitor on AOAA on body weight and systemic markers or organ function in control and DS rats. (A): Body weight of the rats, monitored weekly for two weeks following the initiation of the intraperitoneal administration of saline or AOAA (10 mg/kg/d). (B): At the end of the study, upon animal euthanasia, trunk blood was collected and processed with VetScan® Analyzer for analysis of circulating markers of organ function. Each dot represents one animal per experimental condition. The mean ± SEM per experimental condition was additionally calculated and plotted as bar graphs and lines in subfigures (A) and (B), respectively. Weight data (n =11 per experimental group) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA at each time point and hematological data (n=8 per experimental group) were processed with three-way ANOVA analysis followed by post-hoc analysis with Bonferroni correction. **p≤0.01 shows significant differences between saline-treated DS rats and saline-treated WT rats; ##p ≤ 0.01 shows significant effect of AOAA treatment in Dup(Rno20)Yah rats, indicative of improved organ function.