Figure 1.
Evaluation of ECM coatings for endothelial differentiation of hiPSCs
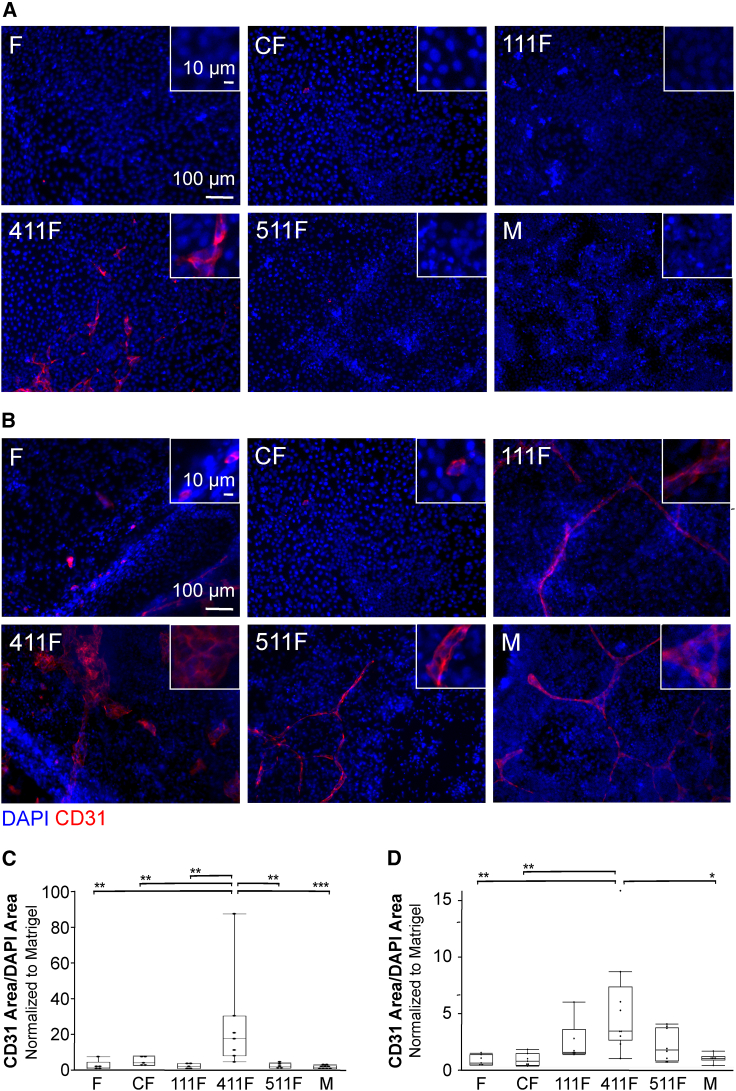
(A) Representative immunofluorescence images showing CD31 staining (red) and DAPI (blue) following differentiation of hiPSCs on ECM-coated plates without the addition of small molecules to drive differentiation. F, fibronectin; C, collagen I; 111, laminin 111; 411, laminin 411; 511, laminin 511; M, Matrigel.
(B) Representative immunofluorescence images showing CD31 staining (red) and DAPI (blue) following differentiation of hiPSCs to endothelial cells using CHIR on ECM-coated plates.
(C) CD31 area normalized to DAPI area following differentiation of hiPSCs on ECM-coated plates in the absence of exogenous factors. Each condition was normalized to the Matrigel control. n ≥ 5 wells per condition, which includes at least three independent experimental replicates per condition. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(D) CD31 area normalized to DAPI area following differentiation of hiPSCs on ECM-coated plates with CHIR addition on days 0 and 1. Each condition was normalized to the Matrigel control. n ≥ 5 wells per condition, which includes at least three independent experimental replicates per condition. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01.