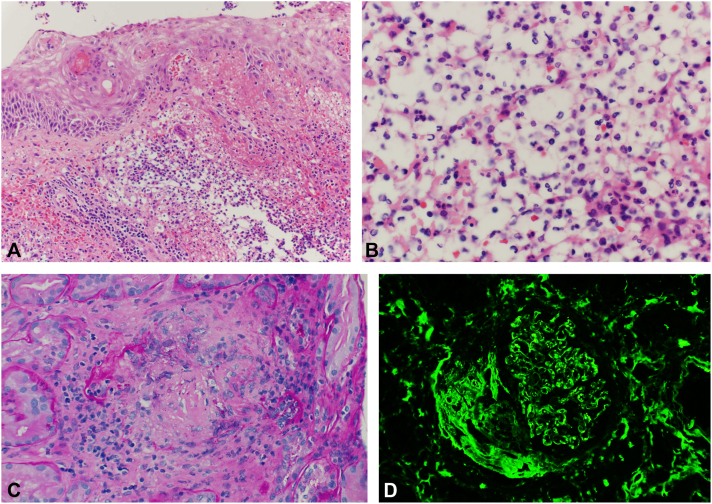
Fig 2.
A, Lesional skin biopsy demonstrating spongiotic epidermis overlying a dermis with marked inflammatory infiltrate consisting of mixed polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cells, as well as hemorrhage and focal dermal necrosis (hematoxylin-eosin stain). B, High-power view of a lesional skin biopsy demonstrating areas of mononuclear cells in the infiltrate (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original magnification: ×40). C, Renal biopsy demonstrating necrotizing granulomas involving the tubulointerstitium; loosely aggregated large epitheliod histiocytic cells and inflammatory lymphocytes, with tissue destruction and central necrosis (Periodic acid–Schiff stain). D, Fibrinogen direct immunofluorescence microscopy of the renal biopsy demonstrated crescent/fibrinoid necrosis as highlighted by positive fibrinogen staining.