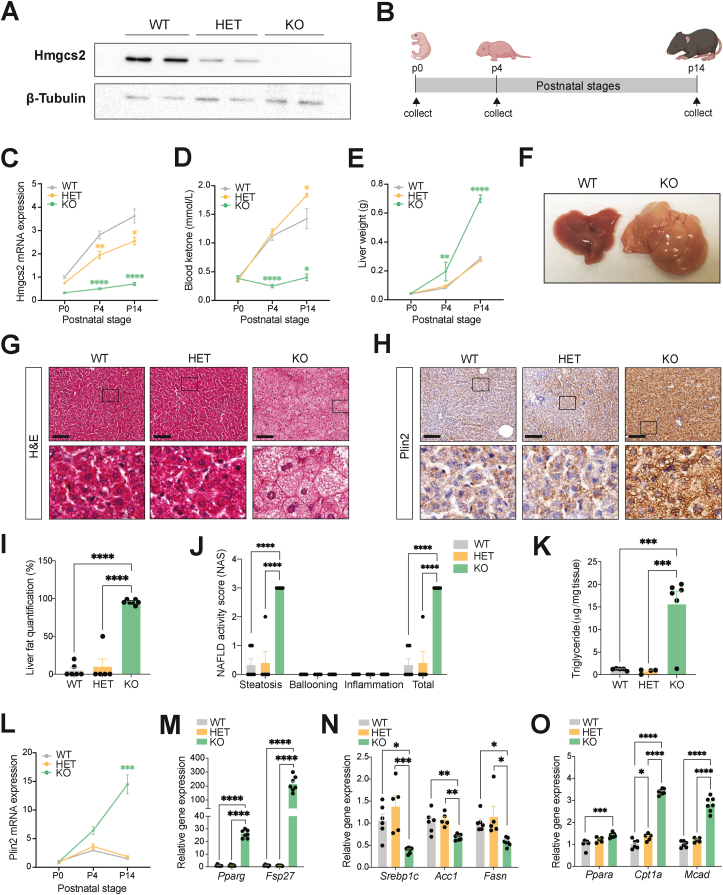
Figure 2.
Ketogenic deficiency through Hmgcs2 knockout results in fatty liver development in postnatal mice. (A) Liver Hmgcs2 protein expression in wild-type (WT), Hmgcs2-heterozygous (HET) and knockout (KO) mice. (B) Schematic representing the postnatal stages of p0, p4, and p14 at which the mice were examined. (C) Hmgcs2 gene expression in the liver, (D) blood ketone levels, and (E) liver weights during postnatal development (p0: WT, n = 5; HET, n = 6–9; KO, n = 6; male and female combined/p4: WT, n = 7–9; HET, n = 6–11; KO, n = 4/p14: WT, n = 4–11; HET, n = 3–9; KO, n = 3–10). (F) Representative image of livers of p14 WT and KO mice. (G) H&E and (H) anti-Plin2 IHC stainings of p14 WT, HET and KO mouse liver sections. Scale bar = 100 μm. Boxes indicate regions of higher magnification. (I) Histological liver fat quantification and (J) NAFLD Activity Score (NAS) (WT, n = 6; HET, n = 5; KO, n = 7). (K) Liver triglyceride concentration of p14 WT, HET and KO mice (WT, n = 5; HET, n = 4; KO, n = 6). (L) Plin2 gene expression in the liver during postnatal development (p0: WT, n = 5; HET, n = 6; KO, n = 6; male and female combined/p4: WT, n = 7; HET, n = 6; KO, n = 4/p14: WT, n = 6; HET, n = 5; KO, n = 7). (M) Lipid accumulation markers (Pparg, Fsp27), (N) lipid synthesis genes (Srebp1c, Acc1, Fasn) and (O) lipid oxidation genes (Ppara, Cpt1a, Mcad) in p14 WT, HET and KO mouse livers (WT, n = 6; HET, n = 5; KO, n = 7). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by one- or two-way ANOVA. ∗P ≤ 0.05; ∗∗P ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗P ≤ 0.001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ 0.0001. (Created with BioRender.com).