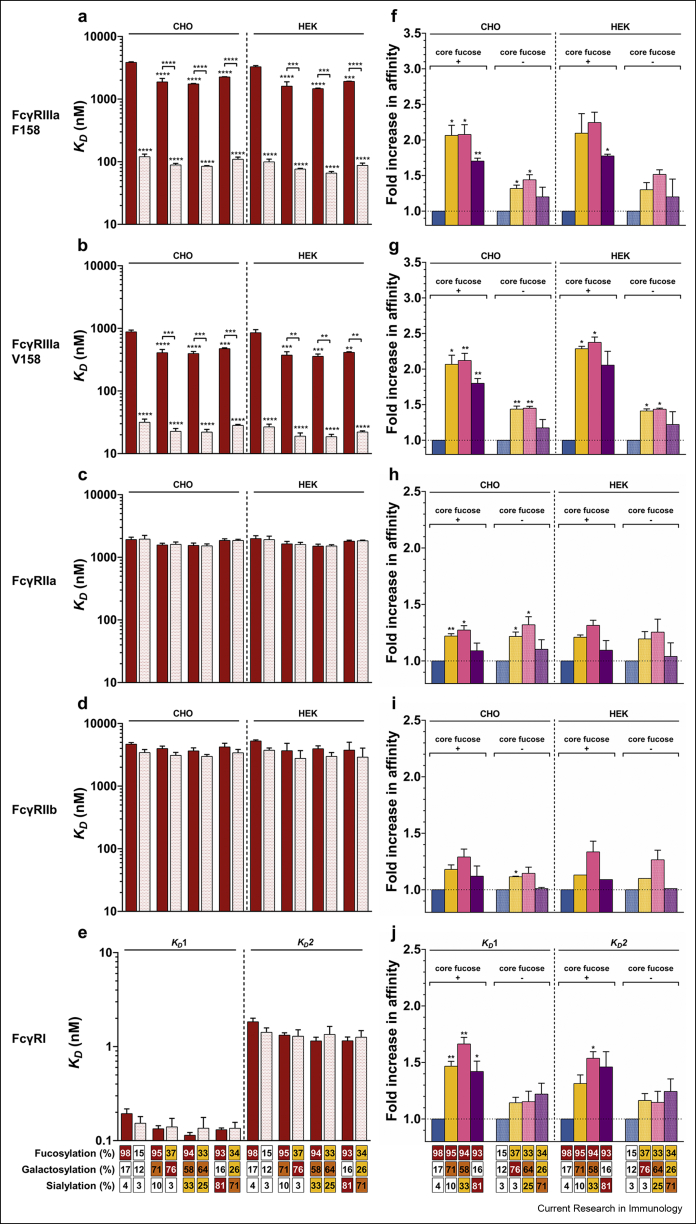
Fig. 6.
Influence of the IgG-Fc N-glycan sugar moieties upon FcγR binding. (a-e) The impact of Fc core fucosylation on FcγR binding affinity. KD values are representative of at least 2 independent experiments for each condition and the standard errors of the mean (SEM) are shown. ∗∗, ∗∗∗ and ∗∗∗∗ denote a statistical significance of p ≤ 0.01, p ≤ 0.001, and p ≤ 0.0001, respectively, as tested by one-way ANOVA using Tukey's multiple comparisons test against TZM, or comparing the fucosylated vs afucosylated forms with the same N-glycan elongation level as indicated by the horizontal lines). (f-j) The impact of terminal sugar moieties (i.e., digalactosylation, mono-α2,6-sialylation and di-α2,6-sialylation) of the IgG1-Fc N-glycan on FcγRs binding relative to TZM (filled column) or TZM RMD (hatched column). The ratios are representative of at least 2 independent experiments and SEM are shown. ∗ and ∗∗ denote a statistical significance of p ≤ 0.05 and p ≤ 0.01, respectively, as tested by a one-sample t-test against a theoretical mean of 1. The abscissa legend describes the percentage of each glycan family.