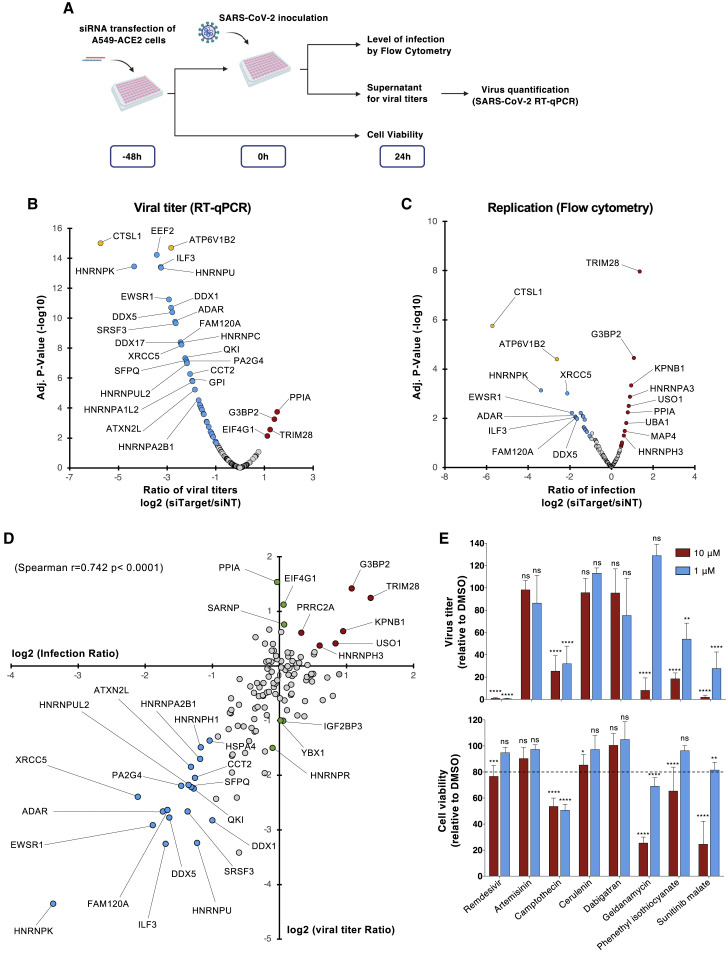
Figure 3.
Functional interrogation of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA interactome and compounds screening
(A) Schematic illustrating the loss-of-function screen procedure.
(B and C) A549-ACE2 cells were transfected with an arrayed siRNA library and challenged with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI 0.05) for 24 h.
(B) Yield of viral particles released in the supernatant of infected cells was quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to the siNT-transfected cells. The data shown are the means of 2 biological replicates (with technical duplicates).
(C) Viral replication was assessed by flow cytometry using anti-N protein monoclonal antibody (mAb) and normalized to the siNT-transfected cells. The data shown are the means of 2 biological replicates (with technical duplicates). Adjusted p values were calculated by 1-way ANOVA with Benjamini and Hochberg correction. Host dependency factors are marked in blue and host restriction factors in are marked in red. Positive controls (CTSL1 and ATP6V1B2) are highlighted in yellow.
(D) Intersection of the data obtained from N protein quantification by flow cytometry and viruses released in the supernatant of infected cells by qRT-PCR. The data shown are the means of 2 biological replicates (with technical duplicates). Host dependency factors are marked in blue and host restriction factors are marked in red.
(E) A549-ACE2 were infected with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI 0.05) in the continuous presence of compounds (10 and 1 μM). Viruses released in supernatant were quantified 24 hpi by qRT-PCR (top panel). Cell viability was assessed in parallel (bottom panel). The data shown are the means ± SDs of 3 biological replicates (with technical duplicates). Significance was calculated using a 2-way ANOVA statistical test with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (n.s, not significant; ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).