Figure 10: Proposed mechanisms of dopamine-mediated serotonin release.
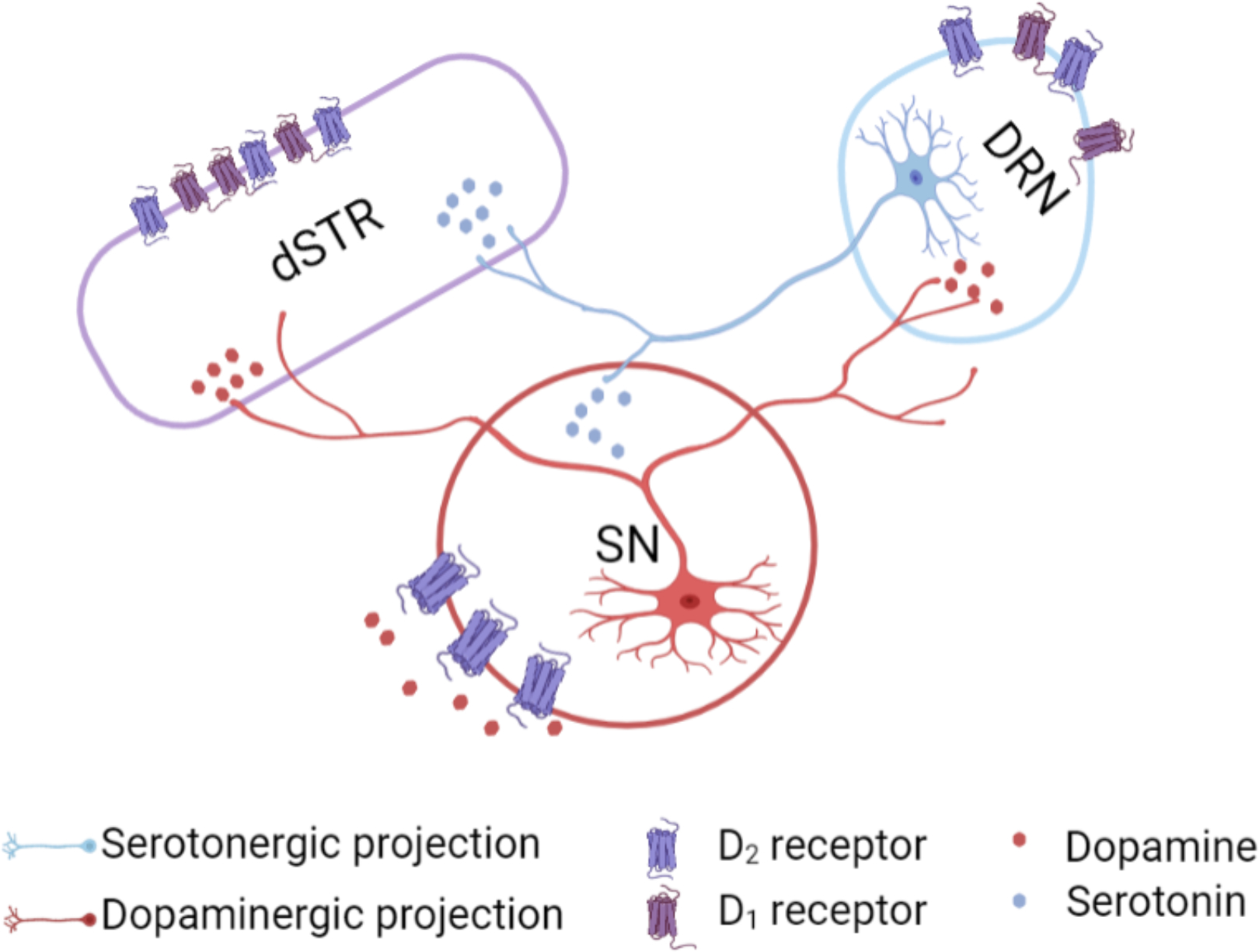
The substantia nigra (SN) sends dense dopaminergic projections to the striatum (nigrostriatal pathway) and to the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN).1 The DRN sends serotonergic projections to dopaminergic cell bodies in the SN and to the striatum.2 We found that dopamine-induced serotonin release was not blocked by local D1- or D2-like receptor inhibition in the striatum. Another possible mechanism for dopamine-mediated serotonin release is that an optogenetically induced increase in dopamine in the SN, which promotes D2 somatodendritic autoreceptor activation3 and subsequent disinhibition of serotonin cell bodies in the DRN, produces serotonin release in the striatum. Alternately, optically induced dopamine release in DRN could act via local D1 or D2-like receptors to increase the probability of firing of DRN serotonin neurons projecting to dSTR.
