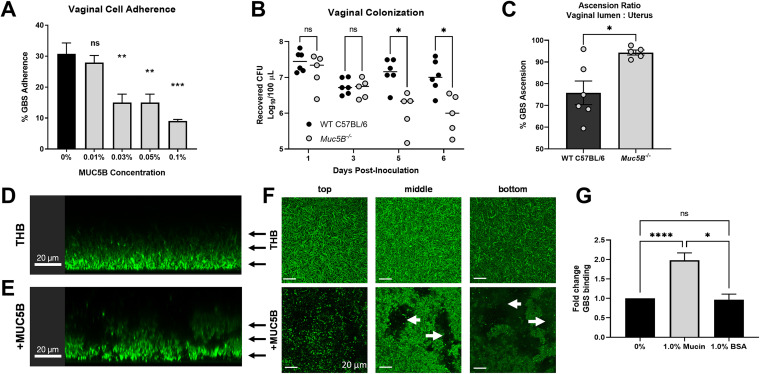
FIG 1.
MUC5B impacts GBS spatial distribution, enhances GBS cell–cell interactions, and promotes vaginal colonization. (A) Adherence of GBS to VK2 cells with 0–0.1% MUC5B. Data represented as mean percent CFU recovered from inoculum. (B) Vaginal persistence of GBS in WT C57BL/6 and Muc5B−/− littermates (n = 6 WT, n = 5 Muc5B−/−, pooled data from two independent experiments). (C) Ascension ratio of GBS from the vaginal lumen to the uterus in C57BL/6 and Muc5B−/− mice 7 days postcolonization. (D–F) Confocal microscopy of GBS cultures grown in (D) Todd Hewitt Broth (THB) or (E) THB with MUC5B. Black arrows denote the vertical plane, with representative images taken from the (F) top, middle, and bottom of the culture. White arrows indicate furrows observed in the samples grown in MUC5B. (G) Binding of GBS to mucins or BSA. Statistical analyses were determined using (A) one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison posttest, (B) two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison posttest, (C) Student’s unpaired, two-tailed t test, and (D) one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison posttest (G). Statistical significance was accepted when p < α, with α = 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.