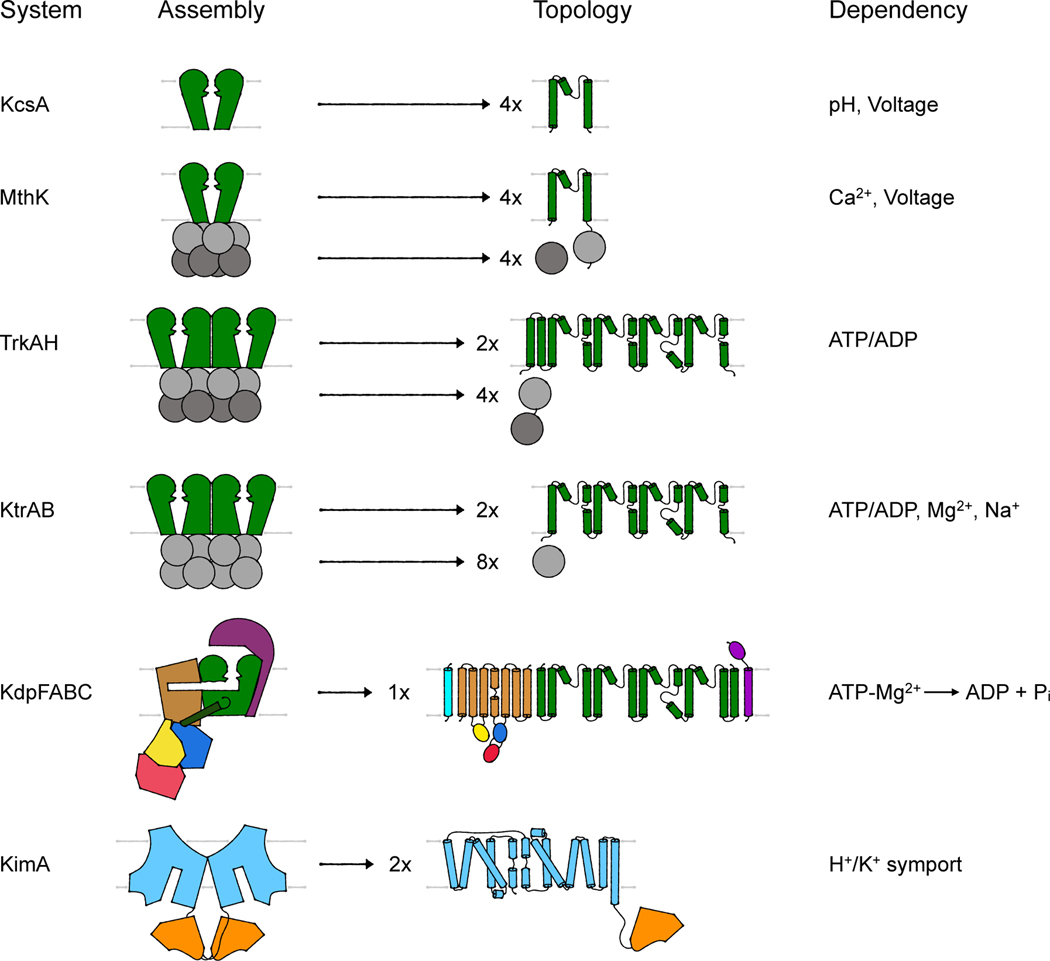
Figure 2. Assembly and topology of bacterial K+-translocating systems.
Overview of the assembly of the different systems discussed. Channel-like subunits/domains are shown in green, RCK subunits/domains in gray, the P-type ATPase KdpB in beige with blue, red and yellow, KdpC in purple, KdpF in cyan, the LeuT-fold domain in light blue, and the adenylyltransferase-like domain in orange. The topologies provide more molecular detail of the transmembrane domains. Characteristic are the M1PM2 domains of the channel-like proteins (green), the insertion of the cytosolic N, P and A domains (red, blue, and yellow, respectively) into loops of the transmembrane domain of KdpB (beige) and the 5+5 inverted repeat of the LeuT-fold domain (light blue) of KimA.