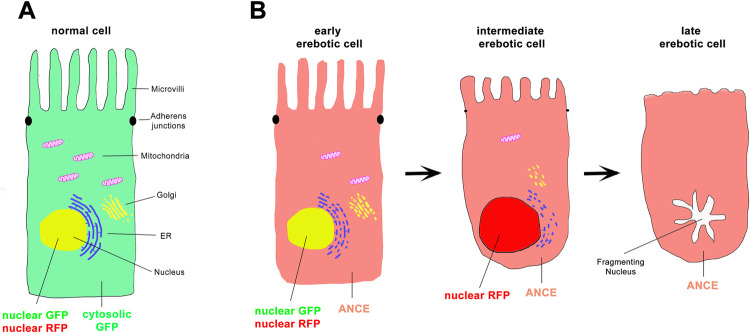
Fig 1. The morphology of erebosis.
(A) Depicted is a normal EC expressing cytosolic GFP (illustrated in green) as well as nuclear GFP and RFP (illustrated in yellow). It also contains a nucleus, organelles (mitochondria, ER, and Golgi), cellular junctions, and microvilli. (B) Erebotic ECs are characterized by loss of proteins, organelles, and nuclear content as well as shorter microvilli. During early erebosis, cytosolic GFP is degraded, while nuclear GFP and RFP persists. Instead, erebotic ECs accumulate ANCE (illustrated in red in the erebotic cell)) through extracellular uptake. ANCE and GFP display a complementary staining pattern. At intermediate erebosis, nuclear GFP is degraded, but nuclear RFP (red) still persists. Erebotic nuclei are larger than normal, and loose nucleoli. At late erebosis, nuclear RFP is also degraded. Fragmented nuclei can be detected via TUNEL labeling. Microvilli are significantly shortened. ANCE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; EC, enterocyte; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.