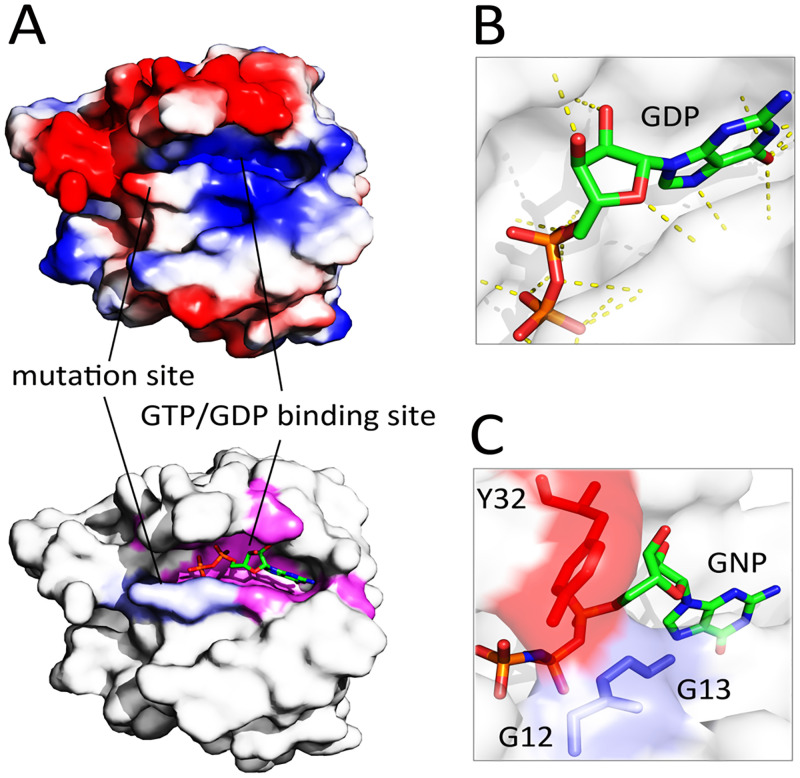
Fig 2. Evaluation of surface charge pattern of the K-RasG12D.
(A) Calculation of the electrostatic surface potential of wild-type K-Ras. The mutation sites 12, 13, and 61 (blue in the below figure) and GTP/GDP binding sites (magenta in the below figure) of the protein are shown with solid lines. The blue, red, and gray colors in the above figure refer to the positively-charged, negatively-charged, and hydrophobic regions, respectively (B) Polar contacts (yellow dotted lines) between GDP and K-RasG12D. (C) A close-up view of the closed conformation of the wild-type GTP-bound K-Ras through direct interaction of G12/13 with Y32.