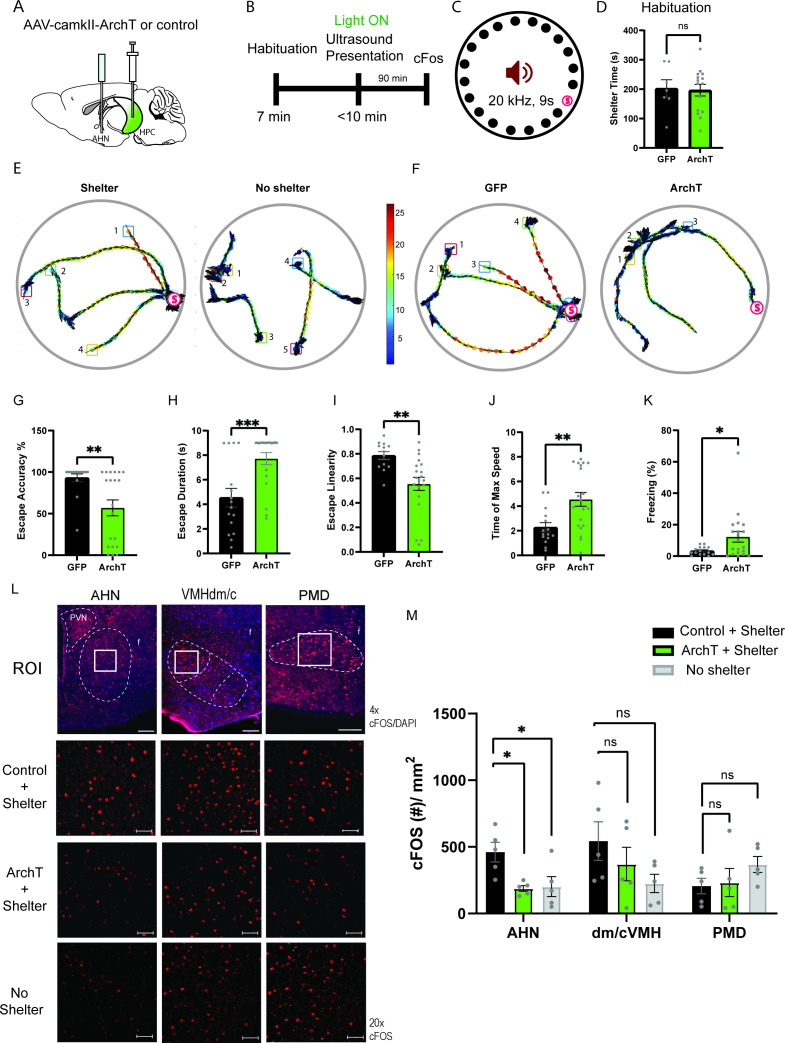
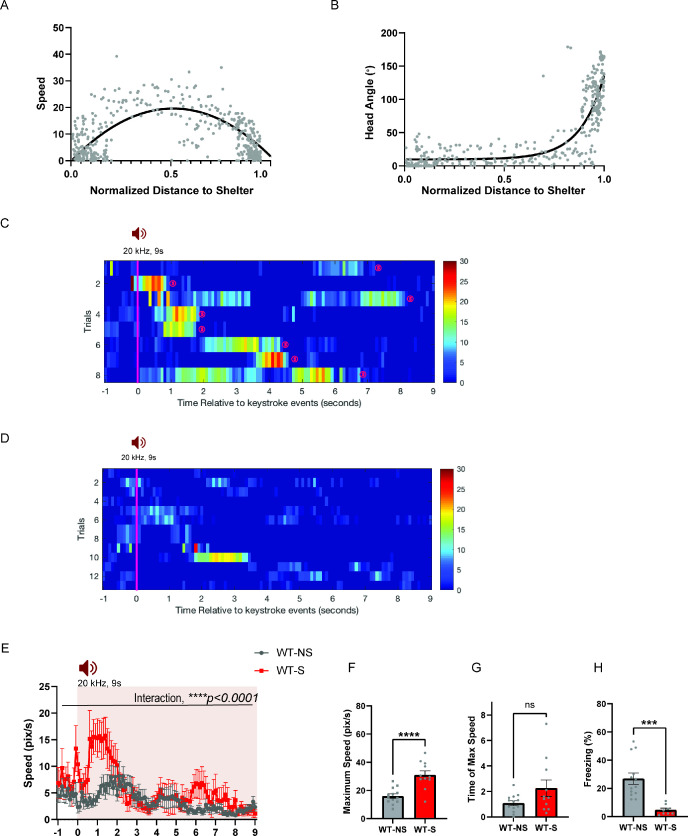
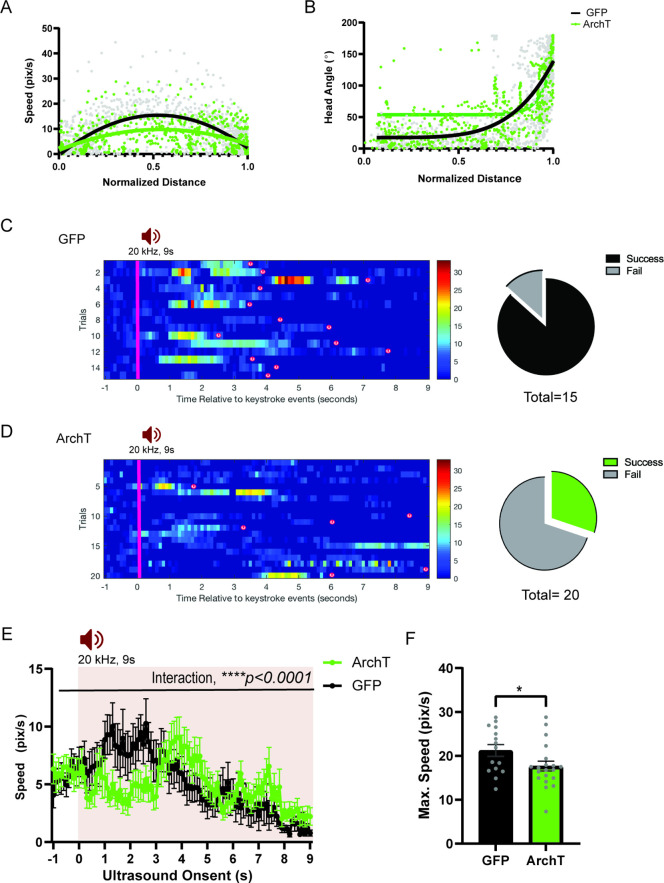
Figure 8. HPC→AHN pathway is necessary for goal-directed escape.
(a) Schematic illustration of optogenetic HPC terminal inhibition in the AHN (GFP N=7 and ArchT N=15). (b) Schematic describing a test paradigm consisting of habituation (7 min) and a threat delivery stage during which ultrasound (20 kHz, 9s) is turned on after mice voluntarily come out of the shelter to induce a shelter-directed escape. (c), Top view of testing apparatus, a modified Barnes maze. ‘s’ denotes the position where a shelter was placed. The red speaker sign denotes the auditory threat played from a speaker above the apparatus centre. (d) Time spent in the shelter during habituation stage (unpaired t-test, t=0.1698, df=20, p=0.8668, NS). (e) Representative ultrasound-evoked escape trajectories for a Wild type (WT) when a shelter is available (left) vs. WT when no shelter is available (right). (f) Representative ultrasound-evoked escape trajectories for a GFP control (left) and ArchT (right). (e,f) Individual threat presentation as a trial is numbered next to a square box, which denotes the animals’ starting position at the beginning of 9 s of 20 kHz sound. Dot color along the trajectory lines reflects animals’ speed. The arrows track animals’ head direction. The heatmap colorbar displays the scale of speed (pix/s). (g) Accuracy of reaching the shelter during escape. (unpaired t-test, t=3.149, df=33, **p=0.0034). (h), The linearity of escape trajectories expressed as the percentage ratio between the length of escape trajectory and a linear distance from escape onset position (i.e. ultrasound onset) to the shelter (unpaired t-test, t=3.266, df=31, **p=0.0027). (i) Time elapsed from the ultrasound onset to the shelter arrival (unpaired t-test, t=3.666, df=33, ***p=0.0008). (j) Time elapsed to reach the maximum speed during escape running to the shelter (unpaired t-test, t=3.134, df=31, **p=0.0036). (k) Time spent in freezing between the ultrasound onset and the shelter arrival (unpaired t-test, t=2.261, df=33, *p=0.0305). (l) c-Fos immunochemical detection across the medial hypothalamic defense system (AHN, VMHdm/c, PMD). First row, representative 4x epi-fluorescence microscope images of the medial hypothalamic defense system in GFP control mice. The regions of interest (ROI, white squares) within AHN, VMHdm/c, and PMD were imaged by confocal microscopy for cell counting. Second and third row: representative 20x confocal images of c-Fos signals in AHN, VMHdm/c, and PMD activated by ultrasound-evoked escapes with a shelter available in GFP (second row) and ArchT mice (third row). Fourth row: representative 20x confocal images of c-Fos signals activated by ultrasound-evoked escapes without shelter in controls. (m) Density of c-Fos signals activated by ultrasound-evoked escapes in AHN, VMHdm/c, and PMD in GFP controls with shelter (black), ArchT mice with shelter (green), and controls without shelter (grey) (N=5 mice for each group). AHN (1-WAY ANOVA, F(2,12)=6.171, *p=0.0144, Sidak’s multiple comparison test, Control Shelter vs. ArchT Shelter, *p=0.0177, Control Shelter vs. Control No Shelter, *p=0.0237), VMHdm/c (one-way ANOVA, F(2,12)=1.824, p=0.2035, NS, Sidak’s multiple comparison test, Control Shelter vs. ArchT Shelter, p=0.5391, NS, Control Shelter vs. Control No Shelter, p=0.1548), PMD (one-way ANOVA, F(2,12)=1.25, p=0.3212, NS, Sidak’s multiple comparison test, Control Shelter vs. ArchT Shelter, p=0.9665, NS, Control Shelter vs. Control No Shelter, p=0.3058, NS). Two-way ANOVA (ROI x treatment, F(4,36)=2.347, p=0.0729, NS, ROI effect, F(2,36) = 1.391, p=0.262, NS, treatment effect, F(2,36)=2.44, p=0.1015, NS, Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). AHN (Control Shelter vs. ArchT Shelter, p=0.1064, NS, Control Shelter vs. No Shelter, p=0.1344, ArchT Shelter vs. No Shelter, p=0.9993, NS), VMHdmd/c (Control Shelter vs. ArchT Shelter, p=0.4470, NS, Control Shelter vs. No Shelter, *p=0.0476, ArchT Shelter vs. No Shelter, p=0.5876, NS), PMD (Control Shelter vs. ArchT Shelter, p=0.9957, NS, Control Shelter vs. No Shelter, p=0.4999, NS, ArchT Shelter vs. No Shelter, p=0.6378, NS). Scale bar = 100 μm for 4x epi-fluorescence microscope images and 10 μm for 20 x confocal images. (PVN, paraventricular nucleus. f, fornix).