Extended Data Fig. 1. Generation of the GSX2 gene reporter hiPS cell line.
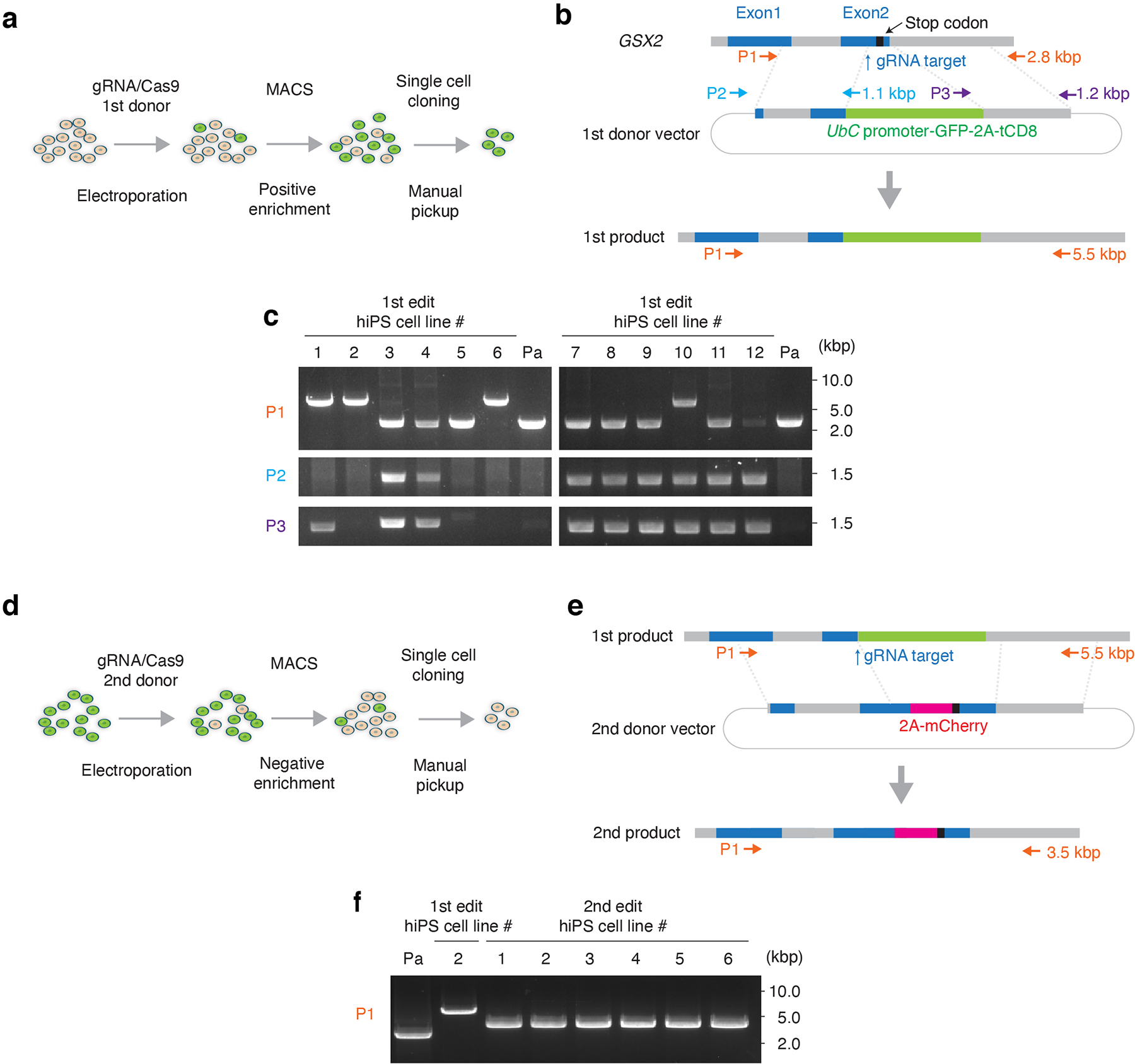
(a) Schematic showing the 1st step of the HDR-based genome editing and (b) the design of the 1st donor plasmids. The genomic sequence around the stop codon of GSX2 gene was replaced by EGFP and the truncated CD8 (tCD8) expression cassette. Arrows indicate the position of primer sets used for the genotyping PCR. Details on genome editing design and the sequence of 1st donor vector are available in Supplementary Table 1. (c) Genotyping and detection of random integration. Primer set 1 (P1) shows targeted integration of the selection marker expression cassette in the GSX2 locus. Primer set 2 (P2) and set 3 (P3) show random integration. For hiPS cell lines #2 and #6, a single 5.5 kb band was detected by P1 and no band was detected by P2 or P3. Subsequent ddPCR showed that 2 copies of exogenous UbC promoter were integrated in #2 and #6. Line #2 was used in the next step of genome engineering. Pa: parental hiPS cell line. (d) Schematic showing the 2nd editing step, and (e) the design of the 2nd donor plasmid. The selection marker expression cassette was replaced by mCherry. Arrows show the primer sets used in the genotyping PCR. The size of amplicons is indicated by arrows. Information on the 2nd donor is available in Supplementary Table 2. (f) Genotyping of the negatively selected lines by PCR. The single 3.5 kbp band indicate biallelic editing. Line #1 from the 2nd editing step was used for further experiments. Full-length, unprocessed gel images for c and f are included in Source Data 1.
