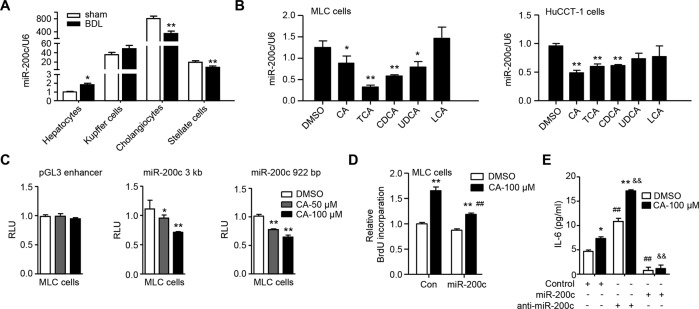
Fig. 1. BAs decrease expression of miR-200c to promote IL-6-mediated cholangiocyte proliferation.
A qPCR of the expression level of miR-200c in primary cells isolated from WT mouse livers 1 week after sham or BDL surgery. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 5/group). *P < 0.05 & **P < 0.01 vs. sham. B qPCR of the expression level of miR-200c in mouse large cholangiocytes (MLC) and human cholangiocarcinoma cells (HuCCT-1). MLC and HuCCT-1 cells were treated with CA (100 µM), TCA (100 µM), CDCA (100 µM), UDCA (100 µM), or LCA (10 µM) for 24 h. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 & **P < 0.01 vs. DMSO. C Transient transfection to determine luciferase reporter activity of miR-200c promoter regulated by CA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 & **P < 0.01 vs. DMSO. D Cell proliferation was determined by BrdU incorporation. MLC cells were transfected with control (con) or miR-200c plasmid for 24 h, followed by the treatment with DMSO or CA for 48 h in the presence of BrdU. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01 vs. DMSO, ##P < 0.01 vs. con-CA. E ELISA of the expression level of IL-6. MLC cells were transfected with control miRNA, miR-200c, or miR-200c inhibitor (anti-miR-200c), and then treated with DMSO or CA (100 µM) for 48 h. The secreted form of IL-6 was determined by ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 & **P < 0.01 CA vs. DMSO; ##P < 0.01 vs. control-DMSO; &&P < 0.01 vs. control-CA.