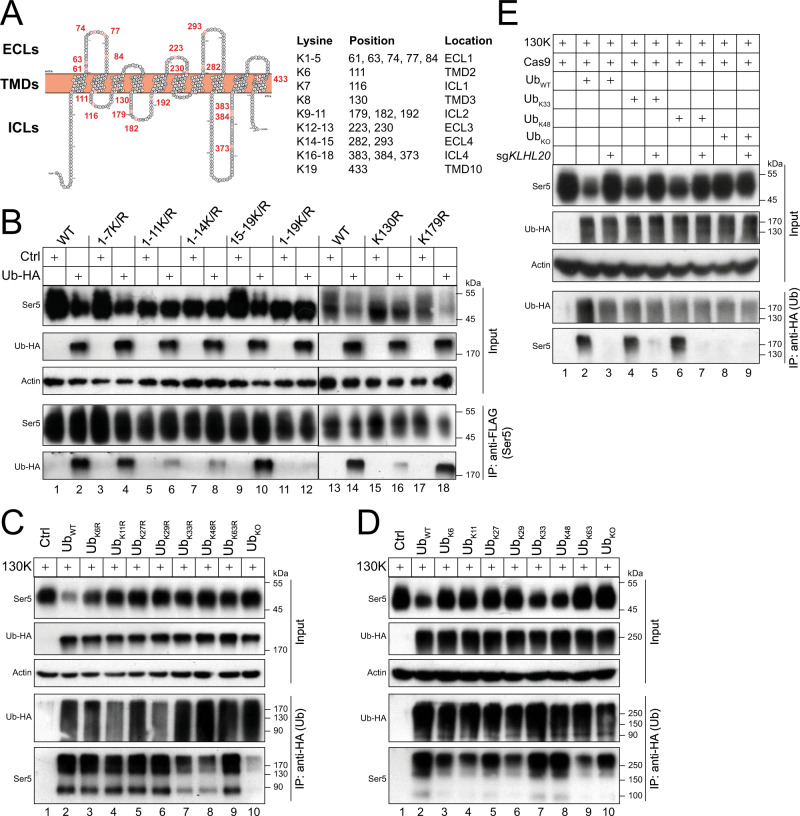
Fig. 2. Identification of lysine 130 (K130) as a critical polyubiquitination site on SERINC5.
A A Ser5 membrane topology model is presented. Five ECLs, 10 TMDs, and 4 ICLs are indicated. Nineteen lysine residues (K1 to K19) are numbered and colored in red. Their distributions into these regions are indicated. Their positions in Ser5 protein are also indicated. The Ser5 membrane topology was predicted by the on-line transmembrane hidden Markov model (TMHMM, v2.0) (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?TMHMM-2.0) and the model was generated by Protter (http://wlab.ethz.ch/protter/start/). ECL, extracellular loop; TMD, transmembrane domain; ICL, intracellular loop. B Ser5 and its lysine mutants were expressed with Ub in HEK293T cells. Ser5 was immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG and levels of polyubiquitinated Ser5 were compared by WB. C The Ser5-130K mutant (130 K) was expressed with Ub and its mutants bearing indicated K-to-R mutations in HEK293T cells. Ectopic Ub was immunoprecipitated by anti-HA and levels of polyubiquitinated Ser5 were compared by WB. D The 130 K mutant was expressed with indicated Ub mutants in HEK293T cells. Ectopic Ub was immunoprecipitated by anti-HA and levels of polyubiquitinated Ser5 were compared by WB. E The 130 K mutant was expressed with indicated Ub mutants in HEK293T cells in the presence or absence of KLHL20-KD. Ectopic Ub was immunoprecipitated by anti-HA and levels of polyubiquitinated Ser5 were compared by WB. All experiments were repeated at least twice, and similar results were obtained. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.