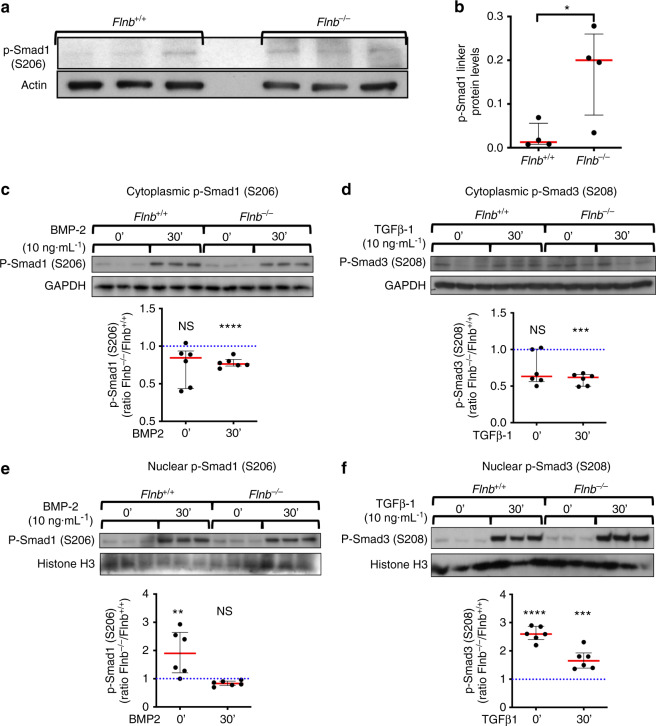
Fig. 3.
Higher levels of linker phosphorylated Smads 1 and 3 were found in the nucleus of Flnb−/− primary chondrocytes. a Western blot of Smad 1 linker phosphorylation levels in protein lysates isolated from Flnb+/+ and Flnb−/− IVDs. b Quantification of Western blot normalized to Actin levels showing a significant increase in Smad 1 linker phosphorylation. n = 3 (each data point contains six IVDs dissected from the thoracic area from a single mouse), NS not significant, *P value < 0.05. c–f Above: Western blots of Flnb+/+ and Flnb−/− cytoplasmic and nuclear protein lysate fractions isolated from primary sternal chondrocytes unstimulated and stimulated with 5 ng·mL−1 TGFβ-1 ligand and 10 ng·mL−1 BMP-2 ligand for 30 min probed with antibodies against Smad 3 linker phosphorylation at the S208 residue, Smad 1 linker phosphorylation at the S206 residue, GAPDH, and histone H3. Below: Quantification of TGFβ-1- and BMP-2-stimulated Western blots normalized against GAPDH (cytoplasmic fractions) and histone H3 (nuclear fractions) levels. The results showed a significant decrease in linker phosphorylated Smad 3 and Smad 1 levels in cytoplasmic fractions but a significant increase in nuclear fractions of Flnb−/− primary chondrocytes. n = 6 (All data points represent biological replicates of Flnb−/− protein lysates, each normalized to a Flnb+/+ control. The dotted blue line in each graph represents the Flnb+/+ protein level, which is set to 1 upon normalization. Significance is determined by comparing Flnb−/− to Flnb+/+), NS not significant, *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001