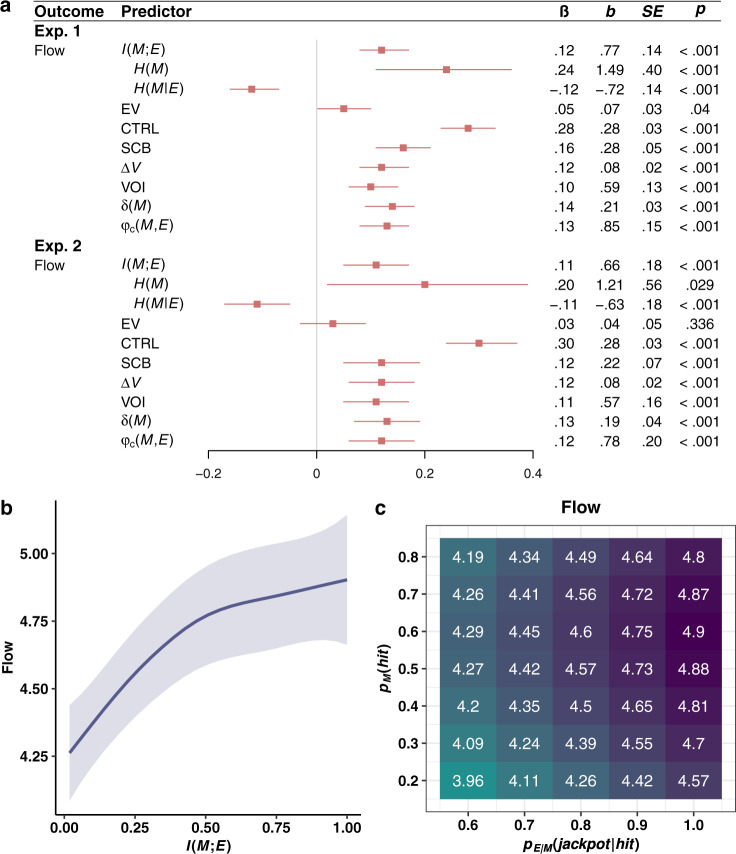
Fig. 2. Flow results from experiments 1 and 2.
a Effect of all variables of interest on flow in experiment 1 (Exp. 1) and experiment 2 (Exp. 2). The variables of interest are , its constituent entropy terms and , expected value (EV), controllability (CTRL), skill-challenge balance (SCB), marginal value (), the value of information (VOI), temporal difference prediction error (), and the correlation between and (). Statistics are derived from linear mixed models (LMMs; two-sided) performed over 720 observations across 365 participants in experiment 1, and 488 observations across 249 participants in experiment 2. Each LMM regresses flow on one variable from the predictor column (with the exception of and H (M|E), which are included in the same model), a nuisance regressor for game order (first game vs. second game), and random subject-level intercepts. Red squares denote standardized regression coefficients, and intersecting red lines represent 95% CIs. No corrections for multiple comparisons were applied. b Results of GAM showing the nonlinear, but monotonically increasing effect of I (M;E) on flow. The solid line denotes expected values and the ribbons denote 95% CIs. c GAM-derived expected values of flow for each combination of pM(hit) and .