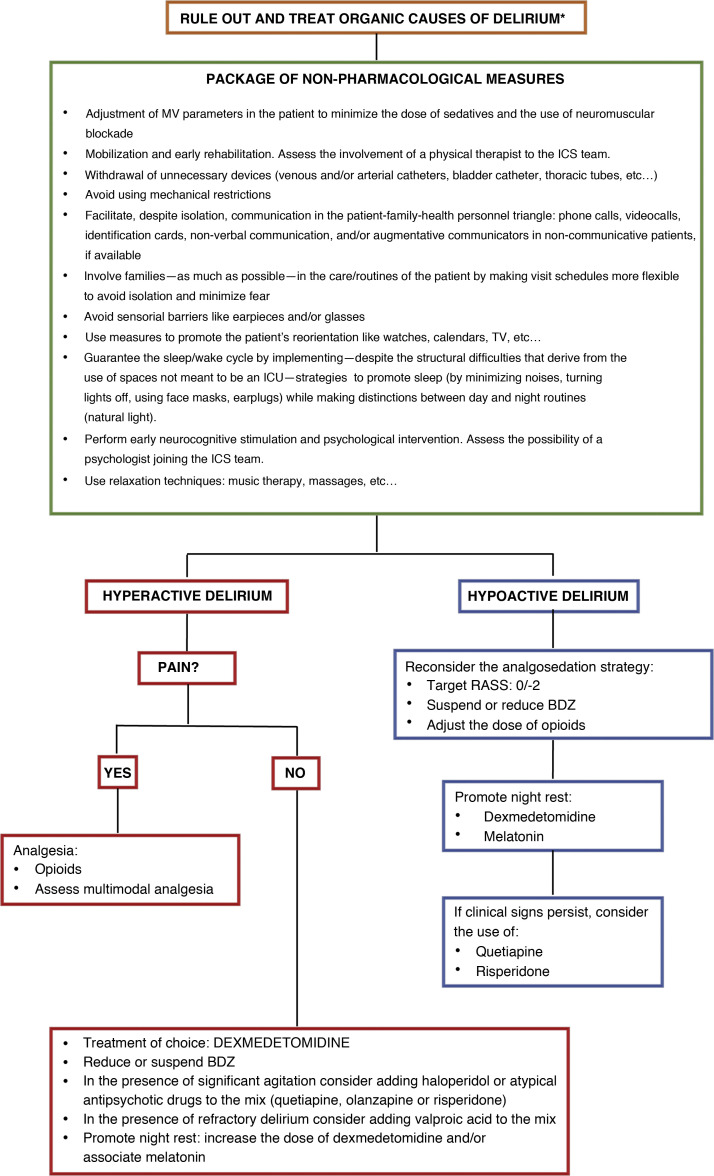
Figure 1.
Treatment of delirium. Non-pharmacological recommendations and pharmacological approach.
* Rule out organic causes of delirium such as hypoxemia, hypercapnia, kidney or liver failure, shock, sepsis, metabolic acidosis or hiydroelectrolytic alterations. Dose of dexmedetomidine for the management of hyperactive delirium: between 0.2 mcg/kg and 1.4 mcg/kg per hour. Dose of haloperidol: 2.5 mg–5 mg IV. It can be repeated every 10 min–30 min up to a cumulative dose of 30 mg. Early dose of quetiapine: 25 mg/8−12 h PO increasing by 25 mg per dose on a daily basis. Early dose of olanzapine: 5 mg/24 h PO. Early dose of risperidone: 1 mg/24 h PO. Dose of valproic acid: 1200–1600 mg/day IV throughout 3–4 takes that can be preceded by a 28 mg/kg load. Dose of melatonin: starting from 2 to 4 mg PO administered 1 to 2 h before night rest.
BDZ, benzodiazepines; RASS, Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale.