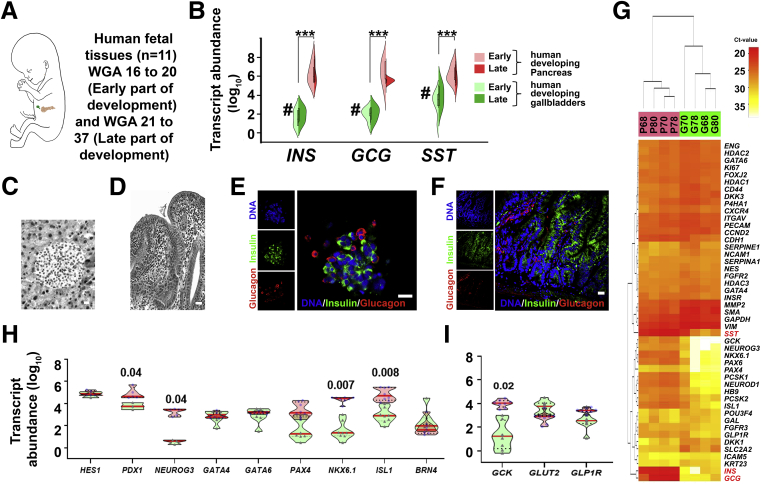
Figure 3.
Human gallbladders show several markers of pancreatic endocrine lineage during embryonic development. (A) Schematic of developing human fetus. Pancreas and gallbladder tissues were available from a total of 11 different fetuses, which were classified as early (<20 WGA, n = 5) or late (>20 WGA, n = 6) development. (B) TaqMan-based real-time qPCR for key pancreatic endocrine hormones (INS, GCG, and SST) in developing human pancreas and gallbladder tissues are plotted based on their developmental stage. Split violin plots compared gene expression in early vs late gallbladders (shades of green) and pancreas (shades of red). The horizontal line within each bar of the split violins represents the median, bars extend to quartiles, and the polygons represent the density of data points and extend to minimum/maximum values. Data were analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis with the Dunn multiple comparisons tests. ∗∗∗P ≤ .001 denotes a significant difference between all pancreas and all gallbladder samples, #P ≤ .01 denotes a significant difference between the early pancreas and early gallbladder samples. (C and D) Representative H&E-stained images of human fetal pancreatic islet and gallbladder sections (in greyscale). (E and F) Immunostaining of insulin (green) and glucagon (red) in the human pancreatic islet and gallbladder epithelial cells from late development. Nuclei (DNA) are shown in blue. (C–F) Scale bar: 20 μm. (G) An unsupervised bidirectional hierarchical plot of 48 important pancreatic genes and transcription factors in the same human fetal pancreas and gallbladder tissues (n = 4; indicated by the sample number) using Euclidean distance metric and average linkage is presented. Heat map represents normalized qPCR Ct values (colored bar) of each gene (gene symbol listed on the right vertical axis) with low Ct values/high expression in orange–red color and higher Ct values/low expression in shades of yellow to white. (H and I) Real-time qPCR data from the human fetal pancreas (n = 5–11) and gallbladder (n = 3–11) for pancreatic genes and transcription factors, analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance with the Fisher's Least Significant Difference (LSD) test. The horizontal solid red line within each polygon represents the median, the horizontal black dotted line represents quartiles, and the polygons represent the density of data points extending to the minimum/maximum values.