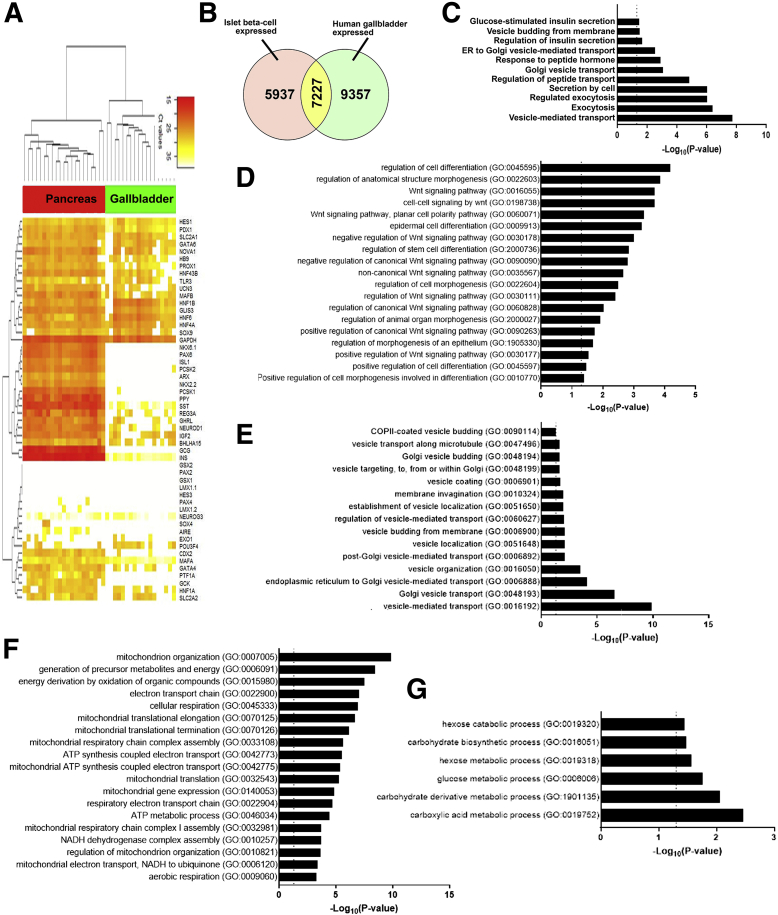
Figure 6.
Gene expression pathways enriched in adult human gallbladder epithelial cells. (A) An unsupervised bidirectional hierarchical cluster of 51 genes known to be associated with or necessary for normal pancreas development/function, profiled in adult human pancreatic islets (red, n = 21) and human gallbladder epithelial cells (green, n = 18) was plotted using Euclidean distance metric and average linkage. The heat map representing normalized qPCR Ct values (color bar) for each gene (listed on right Y-axis) with low Ct values/high expression in orange–red color and higher Ct values/low expression in shades of yellow to white. Data consist of measurement on ViiA7 (INS, GCG, MAFA, NEUROG3, HES1, and PDX1) or using a custom TaqMan OpenArray platform. (B) Venn diagram showing the number of genes common between our bulk gallbladder RNA-seq (n = 6) and the publicly available data set of human islet β-cells (see the Methods section). (C-G) The most significant and relevant Biological Process GO categories enriched in gallbladder cells are presented. Data obtained from RNA-seq was used to identify the gallbladder-expressed genes and total gallbladder transcripts were filtered for β-cell–expressed transcripts obtained from E-GEOD-20966. The X-axis represents −log10 P value, the dotted vertical line represents the significant P value = .05, and relevant pathways are provided on the Y-axis. Pathways involved in (C) endocrine pancreatic β-cell function, (D) development and differentiation, (E) vesicle transport, (F) mitochondrial function, and (G) carbohydrate metabolism are presented. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; COPII, Coat protein complex II; NADH, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.